9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

塞来昔布通过抑制环氧合酶-2 来遏制人肝癌细胞的生长和侵袭
Authors Tai Y, Zhang LH, Gao JH, Zhao C, Tong H, Ye C, Huang ZY, Liu R, Tang CW
Received 10 August 2018
Accepted for publication 23 January 2019
Published 9 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2831—2848
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S183376
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Purpose: Biomarkers
are lacking in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and its
metabolites play crucial roles in the process of inflammation-tumor
transformation. This study was aimed to detect COX-2 expression in HCC tissues
and evaluate the effects of a COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, on biological
behaviors of HCC cell lines in vitro.
Methods: COX-2
expression was detected by immunohistochemistry on a human HCC tissue microarray.
The correlations of COX-2 expression with tumor clinicopathological variables
and overall survival were analyzed. The proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle
distribution, invasion capacity, and related signaling molecules of HCC cells
after incubated with COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib were evaluated in vitro.
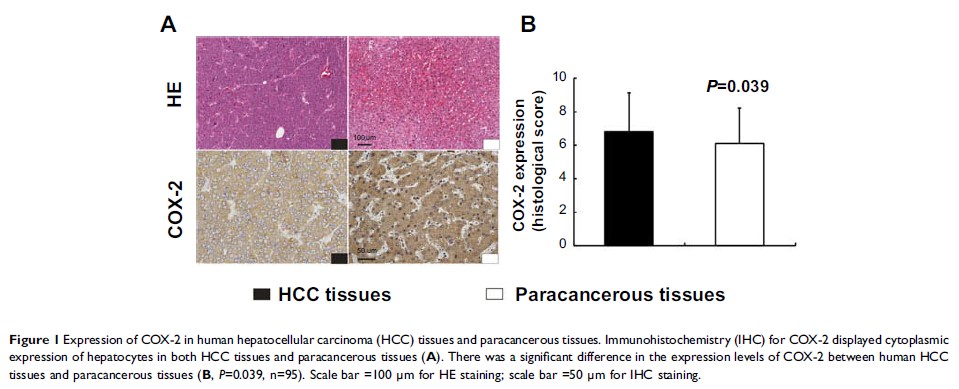
Results: Expression
levels of COX-2 in HCC tissues were significantly higher than those in
paracancerous tissues. The TNM stage III-IV, tumor size >5 cm,
lymphovascular invasion and distant metastasis was higher in high COX-2
expression group compared with that in low COX-2 expression group. Patients
with low COX-2 expression achieved better 5-year overall survival than those
with high COX-2 expression. Treatment with celecoxib was sufficient to inhibit
cell proliferation, promote apoptosis, and induce G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in
HCC cells with concentration- and time-dependent manners. Celecoxib
up-regulated E-cadherin protein through inhibiting COX-2-prostaglandin E2
(PGE2)-PGE2 receptor 2 (EP2)-p-Akt/p-ERK signaling pathway to suppress HCC
cells migration and invasion.
Conclusion: High
COX-2 expression was associated with advanced TNM stage, larger tumor size,
increased lymphovascular invasion and short survival. Targeting inhibition of
COX-2 by celecoxib exhibited anti-tumor activities by suppressing
proliferation, promoting apoptosis, and inhibiting the aggressive properties of
HCC cells.
Keywords: cyclooxygenase-2,
hepatocellular carcinoma, celecoxib, survival