108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

载脂蛋白 A1 和 B 是乳腺癌患者发生眼内转移的危险因素
Authors Liu JX, Yuan Q, Min YL, He Y, Xu QH, Li B, Shi WQ, Lin Q, Li QH, Zhu PW, Shao Y
Received 19 October 2018
Accepted for publication 17 January 2019
Published 9 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2881—2888
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S191352
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objective: Breast
cancer is the most common primary lesion resulting in intraocular metastasis
(IOM). In this study, we investigated the differences between breast cancer patients
with and without IOM, and clarified the risk factors for IOM in patients with
breast cancer.
Methods: A total
of 2,381 patients with breast cancer were included in this study from January
2005 to December 2017. The chi-square test and Student’s t -test were applied
to evaluate differences between the IOM and non-IOM (NIOM) groups. Risk factors
were calculated using binary logistic regression analysis. Receiver operating
curve (ROC) analysis was used to assess the diagnostic value of IOM in patients
with breast cancer.
Results: The IOM
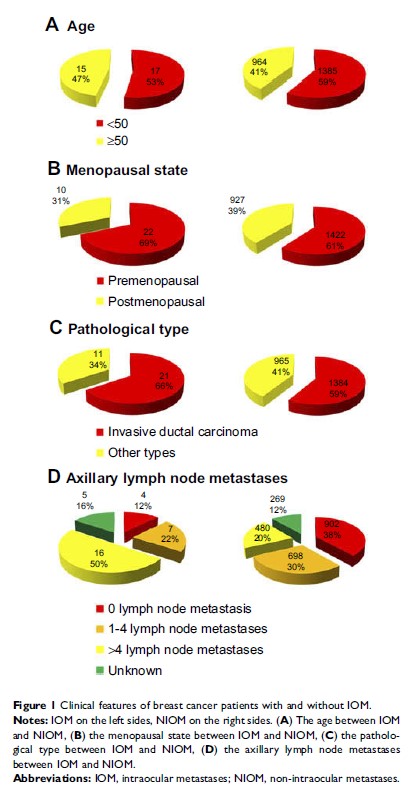
incidence in patients with breast cancer was 1.35%. No significant differences
were detected in age, gender, menopausal status, or histopathology between the
IOM and NIOM groups. The IOM group had more axillary lymph node metastases,
lower ApoA1 and higher ApoB, compared with the NIOM group. Binary logistic
regression indicated that ApoA1 and ApoB were risk factors for IOM in breast
cancer patients (P -values and P -values=0.005, respectively). ROC curve analysis
revealed area under the curve values for ApoA1 and ApoB of 0.871 and 0.633,
using cutoff values of 1.165 and 0.835 g/L, respectively. The sensitivity
and specificity values for ApoA1 were 0.813 and 0.849, respectively, while
those for ApoB were 0.813 and 0.481.
Conclusion: Our data
indicate that ApoA1 and ApoB are risk factors for IOM in patients with breast
cancer and that ApoA1 is more reliable than ApoB at distinguishing IOM from
NIOM in patients with breast cancer.
Keywords: breast
cancer, intraocular metastases, apolipoprotein A1, apolipoprotein B