108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中央和乳头部分的肿瘤位置与患有乳腺癌的女性的受损生存率相关
Authors Ji F, Xiao W, Yang C, Yang M, Zhang L, Gao HF, Lin Y, Zhu T, Cheng M, Li W, Pan W, Zhuang X, Wang K
Received 2 September 2018
Accepted for publication 10 January 2019
Published 9 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2915—2925
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S186205
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: Tumor
location in the breast varies, with the highest frequency in the upper outer
quadrant and lowest frequency in the lower inner quadrant. Nevertheless, tumors
in the central and nipple portion (TCNP) are poorly studied types of breast
cancer; therefore, we aimed to clarify the clinicopathological characteristics
and prognostic features of TCNP.
Methods: Using the
Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database, we identifed 105,037
patients diagnosed with tumor in the breast peripheral quadrant (TBPQ)
(n=97,046) or TCNP (n=7,991). The chi-squared test was used to compare
categorical variables across TCNP and TBPQ. Cox proportional hazard models with
hazard ratios were applied to estimate the factors associated with prognosis.
Results: The median
follow-up was over 43 months. Compared with TBPQ, TCNP patients were
signifcantly older (age ≥66 years: 40.4% vs 34.1%, P<0.001), with larger
tumor sizes (>20 mm size: 46.9% vs 37.3%, P<0.001), higher proportions of
TNM stage II–III (18.6% vs 9.9%, P<0.001), and more mastectomies (58.1% vs
37.8%, P<0.001). The breast cancer-specifc survival (BCSS)/overall survival
(OS) rate was signifcantly worse for TCNP than for TBPQ. Multivariate Cox
analysis showed a higher hazard ratios for TCNP over TBPQ (BCSS: hazard ratios
=1.160, P=0.005, 95% CI: 1.046–1.287; OS: hazard ratios =1.301, P<0.001, 95%
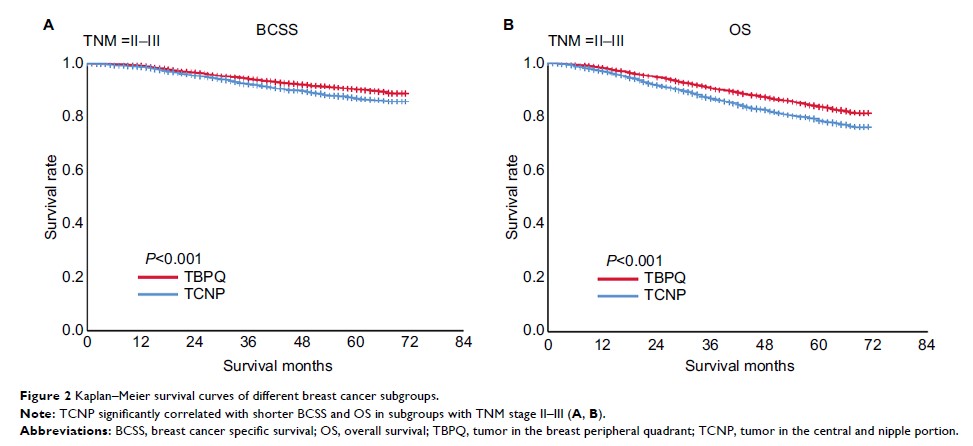
CI: 1.211–1.398). A subgroup analysis revealed inferior outcomes for TCNP in
TNM stage II–III and breast subtype subgroup. Multivariate logistic regression
indicated that TCNP was an independent contributing factor to LN
metastasis.
Conclusions: TCNP was
associated with older age, larger tumor size, higher TNM stage, and lymph node
metastasis. Compared with TBPQ, TCNP had adverse impacts on BCSS and OS.
Keywords: tumor in
the central and nipple portion, tumor in the breast peripheral quadrant,
prognosis, lymph node metastasis