9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

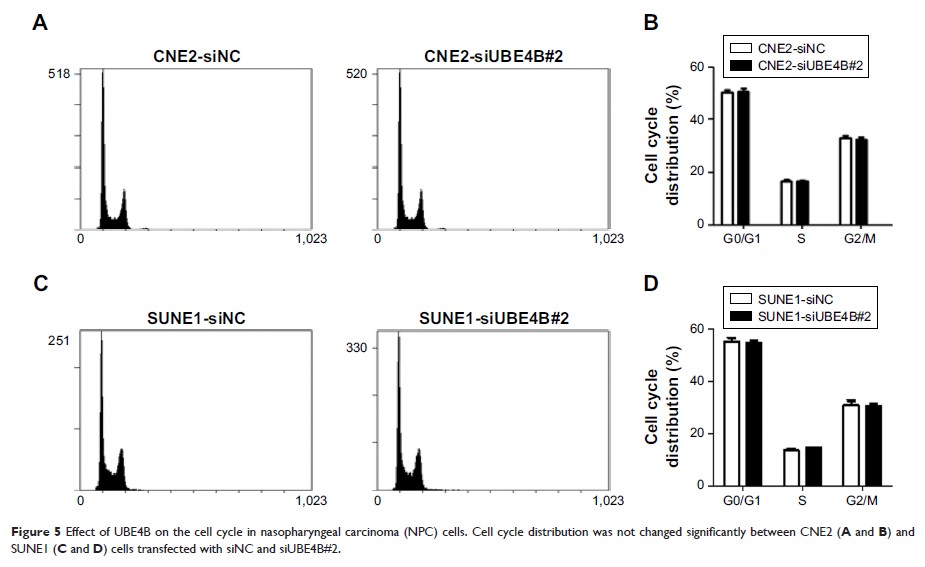
沉默 UBE4B 通过激活 caspase3 和 p53 诱导鼻咽癌细胞凋亡
Authors Weng C, Chen Y, Wu Y, Liu X, Mao H, Fang X, Li B, Wang L, Guan M, Liu G, Lu L, Yuan Y
Received 27 November 2018
Accepted for publication 4 February 2019
Published 8 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2553—2561
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S196132
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Aim: The human
ubiquitination factor E4B (UBE4B) gene is frequently amplified in some solid
cancers. However, the role of UBE4B in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) has not
yet been investigated.
Methods: Firstly,
we analyzed the expression of UBE4B in NPC samples using real-time quantitative
PCR and Western blot analysis. After knocking down UBE4B using small
interfering RNA technology, the functions of UBE4B on cell proliferation,
apoptosis, and cell cycle, as well as underlying mechanism, were investigated.
Results: Compared
with matched adjacent non-tumor tissues, both protein and mRNA levels of UBE4B
were much higher in most NPC cancerous specimens. Deficiency of UBE4B could
significantly inhibit tumor cell growth and induce cell apoptosis. Knocking down
UBE4B could promote the expression of cleaved caspase3 and p53, and inhibition
of caspase3 could prevent cell apoptosis induced by the deficiency of UBE4B.
Conclusion: These
results indicate that expression of UBE4B was higher in most NPC tissues
compared to adjacent non-tumoral tissues, and that knockdown of UBE4B inhibited
the cell growth and induced apoptosis in NPC cells. This process was regulated
by the activation of caspase3 and p53. Thus, UBE4B gene might act as a
potential molecular target to develop novel strategy for NPC patients.
Keywords: UBE4B,
nasopharyngeal cancer, apoptosis, caspase3, p53