9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

乳腺癌中 FOXP4 的上调通过促进 EMT 利于迁移和侵袭
Authors Ma T, Zhang J
Received 21 October 2018
Accepted for publication 24 January 2019
Published 8 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2783—2793
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S191641
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Background: Family of
forkhead box transcription factors has been found to play key roles in multiple
types of cancer.
Materials and methods: Our study
is to decipher the effects of FOXP4 in human breast cancer (BC). Quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analyses were performed to
determine the mRNA and protein expressions of FOXP4 in BC tissue samples and
cell lines. The gain and loss of function assay were used to explore the
detailed roles of FOXP4 in breast cell lines, including MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7
cells. Its effect on BC growth, migration, and invasion were evaluated by
colony formation assay, CCK-8 assay, wound-healing assay, and transwell
invasion assay, respectively.
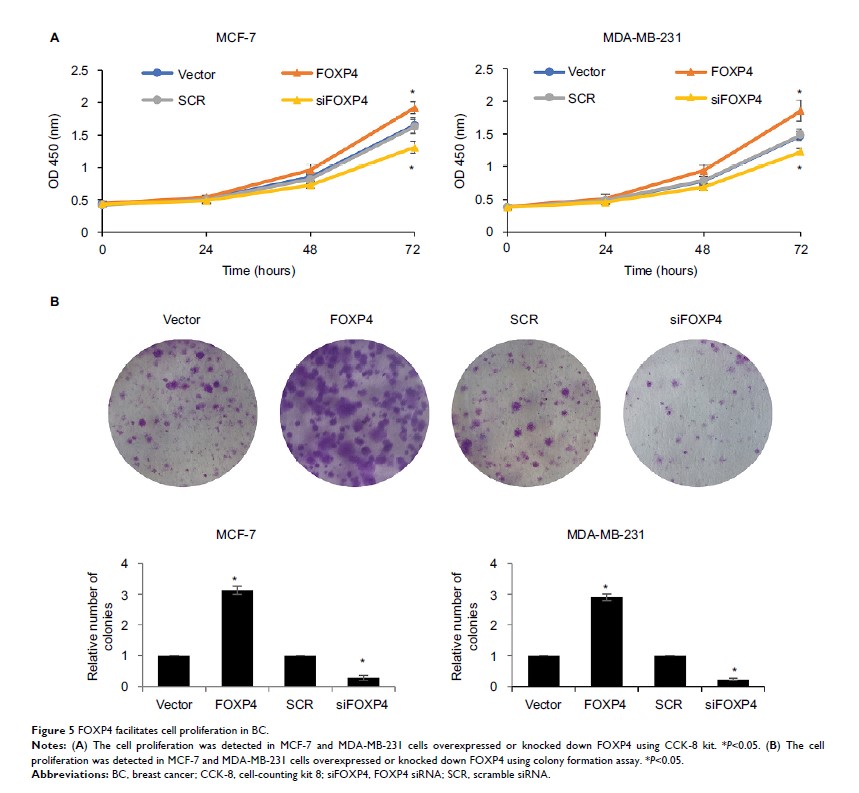
Results: Our
findings revealed that FOXP4 promotes cell proliferation, migration, as well as
invasion of BC cells. Furthermore, FOXP4 also facilitates
epithelial–mesenchymal transition. ChIP, qChIP assay, and dual luciferase
reporter assay were used to examine whether Snail is a downstream target of
FOXP4. Moreover, overexpression of Snail could partially rescue the effects of
FOXP4 inhibition on cancer cell migration and invasion.
Conclusion: Our
findings revealed that FOXP4 is a critical regulator in BC.
Keywords: FOXP4,
EMT, Snail, migration, breast cancer