9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

转运蛋白衍生的细胞穿透肽递送 siRNA 以抑制流感病毒在体内的复制
Authors Zhang C, Ren W, Liu Q, Tan Z, Li J, Tong C
Received 21 November 2018
Accepted for publication 16 February 2019
Published 4 April 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1059—1068
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S195481
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Cristiana Tanase
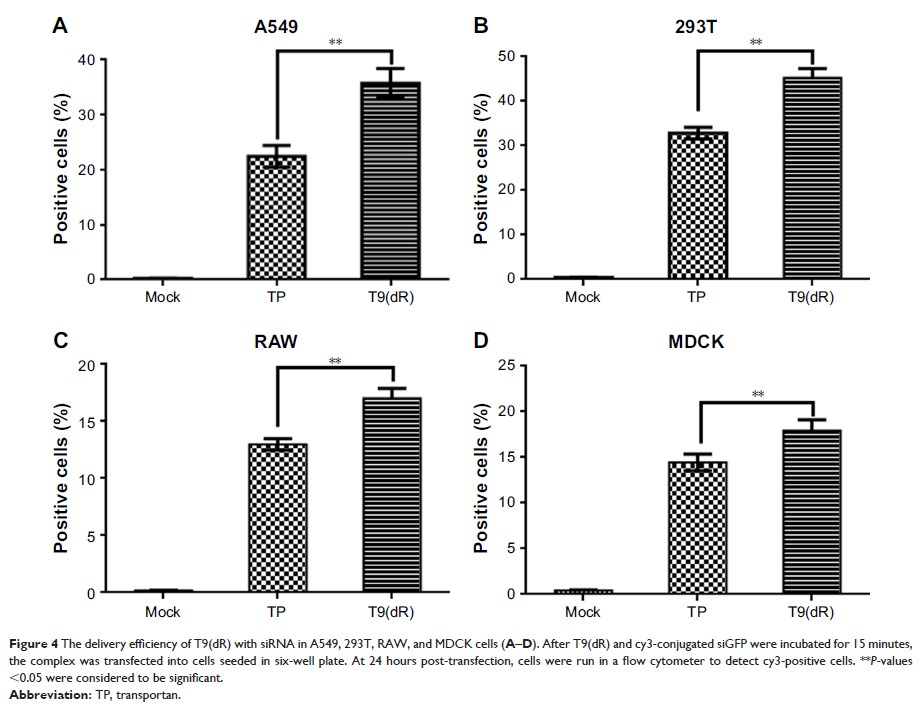
Introduction: In this
study, we report on the development of an effective delivery system for siRNAs;
a novel cell-penetrating peptide (CPP), T9(dR), obtained from transportan (TP),
was used for in vivo and in vitro testing.
Methods: In this
study, toxicity of T9(dR) and TP and efficient delivery of siRNA were tested in
293T, MDCK, RAW, and A549 cells. Furthermore, T9(dR)- and TP-delivered siRNAs
against nucleoprotein (NP) gene segment of influenza virus (siNP) were studied
in both cell lines and mice.
Results: Gel
retardation showed that T9(dR) effectively condensed siRNA into nanoparticles
sized between 350 and 550 nm when the mole ratio of T9(dR) to siRNA was
≥4:1. In vitro studies demonstrated that T9(dR) successfully delivered siRNA
with low cellular toxicity into several cell lines. It was also observed that
T9(dR)-delivered siRNAs inhibited replication of influenza virus more
efficiently as compared to that delivered by TP into the MDCK and A549 cells.
It was also noticed that when given a combined tail vein injection of siNP and
T9(dR) or TP, all mice in the 50 nmol siNP group infected with PR8 influenza
virus survived and showed weight recovery at 2 weeks post-infection.
Conclusion: This
study indicates that T9(dR) is a promising siRNA delivery tool with potential
application for nucleotide drug delivery.
Keywords: cell-penetrating
peptide, CPP, siRNA, inhibition, influenza virus, IV, transportan,
nucleoprotein, NP