9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

葡萄糖响应性介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子产生过氧化氢,用于协同性癌症饥饿疗法和化学治疗
Authors Du X, Zhang T, Ma G, Gu X, Wang G, Li J
Received 25 November 2018
Accepted for publication 4 March 2019
Published 2 April 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 2233—2251
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S195900
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
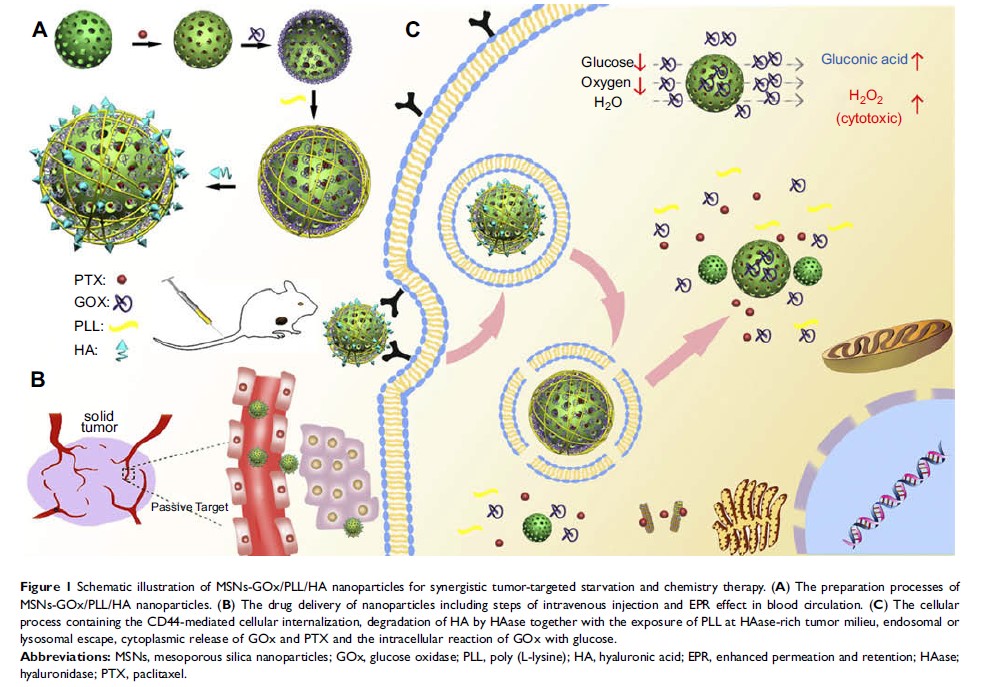
Background: The
combination of novel starving therapy with chemotherapy is one of the most
promising strategies to achieve an effective antitumor activity.
Methods: Herein,
we developed a multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSNs-GOx/PLL/HA)
coated with poly (L-lysine) (PLL) and hyaluronic acid (HA) for co-delivery of
glucose oxidase (GOx) and anticancer drug paclitaxel (PTX) for cancer treatment
for the first time. Compared to single chemotherapy, introduction of GOx would
not only selectively trigger the consumption of intracellular glucose, leading
to the interruption of energy supply, but also elevat the endogenous H2O2 level,
inducing stronger therapeutic effects.
Results: The novel
drug delivery system possessed desirable particle diameter of 40 nm and
exhibited a pH-sensitive drug release behavior. An in vitro cellular uptake
study indicated that MSNs-GOx/PLL/HA nanoparticles effectively enhanced the
cellular uptake of drug in an apparently CD44 receptor-dependent manner, and
delivered more cargo into cytoplasm via endolysosomal escape effect in presence
of PLL. The nanoplatform has also demonstrated amplified synergistic
therapeutic effects for remarkable tumor inhibition in a xenograft animal tumor
model.
Conclusion: Consequently,
the developed synergistic starving-like/chemotherapy may provide a potential
platform for next generation cancer therapy.
Keywords: combination
therapy, glucose oxidase, hyaluronic acid, pH-sensitivity, nanomedicine