108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

组蛋白去乙酰化酶 6 出现过表达并通过调节 MAPK/ERK 信号途径促进结肠癌的肿瘤生长
Authors Zhang SL, Zhu HY, Zhou BY, Chu Y, Huo JR, Tan YY, Liu DL
Received 17 November 2018
Accepted for publication 1 March 2019
Published 2 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2409—2419
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S194986
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
Purpose: To
investigate the expression of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) in colon cancer and
its role in colon cancer cell growth and migration.
Materials and methods: We
detected the expression of HDAC6 in a colon cancer tissue chip using immunochemical
staining, and analyzed the difference in HDAC6 expression between cancer and
adjacent noncancerous tissues. Then, we explored the relationship between HDAC6
expression and patients’ clinicopathological characteristics and prognoses. In
adidition, the role of HDAC6 in colon cancer cell growth and migration, as well
as its potential related signal pathway, through HDAC6 knockdown was explored.
Results: The
immunochemical score of HDAC6 expression was higher in cancer tissue than in
the adjacent noncancerous tissue (4.54 vs 3.08, P <0.005);
similarly, as well as the rate of high HDAC6 expression was higher in cancer
tissue than in the adjacent noncancerous tissue (71.1% vs 40.9%, P <0.001).
Patients showing high HDAC6 expression had a shorter overall survival time.
Additionally, Cox regression analysis showed that high HDAC6 expression was an
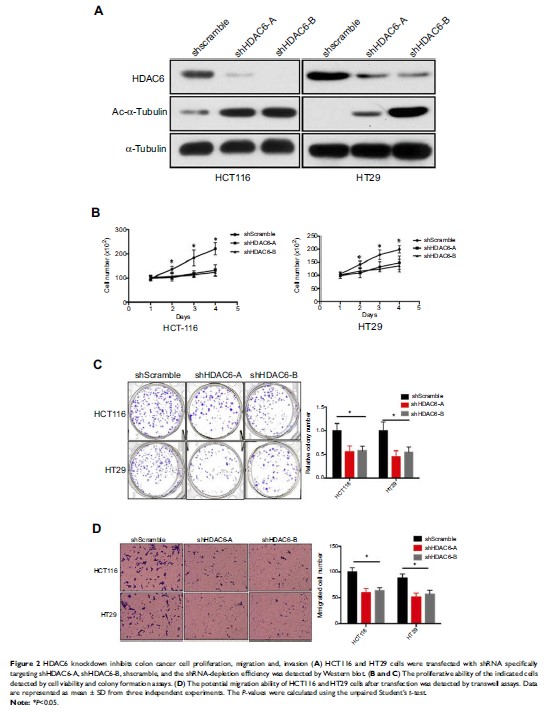
independent risk factor for poor prognosis. HDAC6 knockdown decreased cell
viability, colony formation, and number of migrated colon cancer cells (HCT116
and HT29); the expression of p-MEK, p-ERK, and p-AKT was also decreased, but
had no influence on MEK, ERK, and AKT expression.
Conclusion: HDAC6 is
highly expressed in colon cancer and associated with a poor prognosis. HDAC6
knockdown inhibits colon cancer cell growth and migration, partly through the
MAPK/ERK pathway.
Keywords: colon
cancer, cell growth and migration, histone deacetylase 6, MAPK/ERK pathway, CRC
prognosis