9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

生长分化因子-15 调节胶质母细胞瘤中的 PD-L1 表达
Authors Peng H, Li Z, Fu J, Zhou R
Received 24 October 2018
Accepted for publication 20 February 2019
Published 2 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2653—2661
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S192095
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Lu-Zhe Sun
Background: Gliomablastoma
multiforme (GBM) is the most fatal form of all brain cancers in human with no
successful treatment available. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a
coinhibitory ligand predominantly expressed by tumor cells. Growth
differentiation factors (GDFs) are a subfamily of proteins belonging to the
transforming growth factor beta superfamily that have functions predominantly
in tissue development and cancer.
Purpose: To
investigat the expression of GDFs in GBMs, and explored the potential
regulatory role of GDFs on PD-L1 expression in GBMs.
Methods: GEO2R
program were analyzed for the mRNA expression data of GDFs in GSE4290 dataset.
Analysis of TCGA GBM datasets were further determined the relationship between
GDFs and PD-L1. Western blot Western blot was used to detect the expression of
PD-L1 in GBM cell lines.
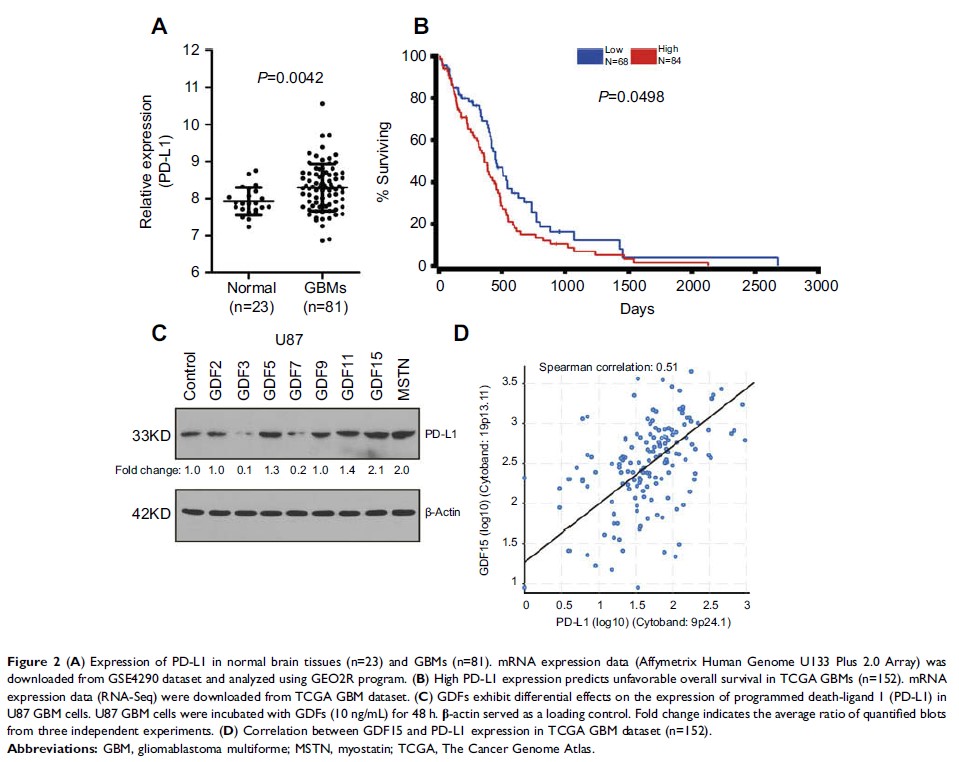
Results: GDFs displayed
differential patterns of expression with GDF15 and myostatin (MSTN) highly
enriched in GBM tissues. We also identified GDF15 as a novel regulator that
induces PD-L1 expression in GBM cells. Consistently, GDF15 expression
correlated with PD-L1 in TCGA GBM dataset. Further, GDF15 enhanced PD-L1
expression via Smad2/3 pathway in GBM cell line U87, U251 and SHG44, which was
inhibited by Smad2/3 inhibitor SIS3. Knockdown of GDF15 attenuated Smad2/3
signaling and reduced PD-L1 expression in A172 and GIC6 glioma cells.
Conclusion: GDF15 might be
a novel regulator of PD-L1 expression in GBMs; targeting GDF15/PD-L1 pathway
might be a promising therapeutic approach for GBM patients.
Keywords: PD-L1,
GDF, GDF15, GBM, immunotherapy