9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

NECTIN4 通过激活 AKT 促进乳头状甲状腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并触发 EMT
Authors Hao RT, Zheng C, Wu CY, Xia EJ, Zhou XF, Quan RD, Zhang XH
Received 10 October 2018
Accepted for publication 7 March 2019
Published 2 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2565—2578
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S190332
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Abstract: Papillary
thyroid cancer (PTC) is the most frequent type of malignant thyroid cancer, but
its molecular mechanisms remain unknown. To better understand the tumorigenesis
and progression of PTC, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of the
whole-transcriptome resequencing of paired PTC and normal thyroid tissues.
Nectin cell adhesion molecule 4 (NECTIN4) was significantly overexpressed in
thyroid carcinoma compared with that in matched normal tissue. We also assessed
the relation between the expression level of NECTIN4 and the
clinicopathological features of PTC in The Cancer Genome Atlas database, and
results showed that upregulated NECTIN4 is associated with lymph node
metastasis (P <0.001)
and tumor size (P =0.017).
The biological function of NECTIN4 was also investigated by using the PTC cell
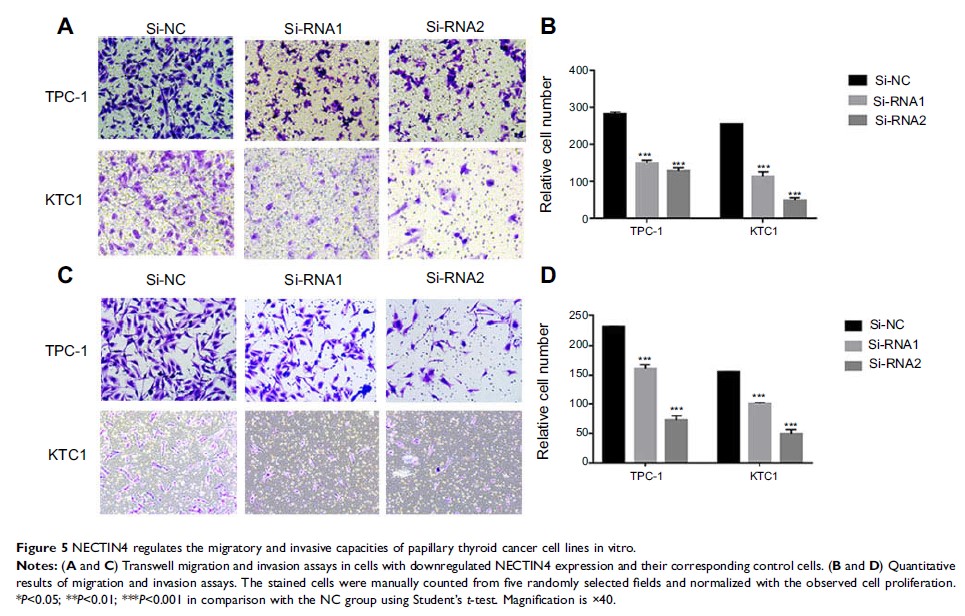
lines TPC-1 and KTC-1. In vitro experiments demonstrated that NECTIN4
downregulation significantly inhibits the colony formation, proliferation,
migration, and invasion of PTC cell lines. NECTIN4 could modulate the
expression of epithelial–mesenchymal transition-related proteins via the
PI3K/AKT pathway, and SC79, an AKT phosphorylation activator, could reverse the
si-RNA knockdown effect. In addition, after the use of AKT inhibitors (LY
294,002), we found that SiRNA have similar effect with AKT inhibitors. Taking
the results together, the current study shows that NECTIN4 has important
biological implications in the tumorigenesis and metastasis of PTC and may be a
potential therapeutic target for the disease.
Keywords: NECTIN4,
PTC, AKT