108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用于口服递送绞股蓝总皂苷、含有胆盐的纳米结构脂质载体的配方设计、表征和体外和体内评价
Authors Yang G, Wu F, Chen M, Jin J, Wang R, Yuan Y
Received 16 November 2018
Accepted for publication 9 February 2019
Published 1 April 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 2267—2280
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S194934
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Gypenosides
(GPS) have been used as traditional medicine for centuries with various
pharmacological effects. However, its therapeutic effects were restricted owing
to the poor lipid and water solubility and low absorption. This study aimed to
develop nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) containing a bile salt formulation
(sodium glycocholate, SGC) for GPS, and to evaluate the potential of the
GPS-SGC-NLCs as an oral delivery system.
Methods: The
preparation of GPS-SGC-NLCs was investigated using a single-factor test and a
central composite design of response surface methodology. In vitro release and
pharmacokinetics studies were used to evaluate the dissolution and
bioavailability of GPS. Furthermore, In vivo imaging and in situ intestinal
perfusion studies were performed to investigate the absorption of the
preparations in the gastrointestinal tract.
Results: The
optimised formulation yielded nanoparticles with an approximate diameter of
146.7 nm, polydispersity of 0.137, zeta potential of -56.0 mV, entrapment
efficiency of 74.22% and drug loading of 4.89%. An in vitro dissolution
analysis revealed the sustained release of contents from GPS-SGC-NLCs over 48 h
with 56.4% of the drug released. A pharmacokinetic analysis revealed an
8.5-fold increase of bioavailability of the GPS-SGC-NLCs compared with GPS
powder. In vivo imaging and in situ intestinal perfusion studies showed that
SGC-NLCs could significantly increase the absorption of GPS in intestinal
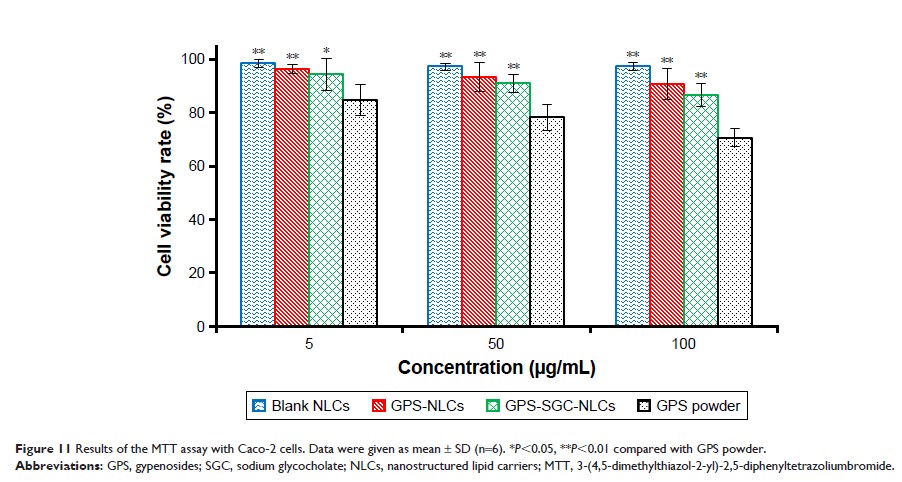
tract. In vitro cytotoxicity evaluated using Caco-2 cells demonstrated that
GPS-SGC-NLCs decrease the cytotoxicity of the drug.
Conclusion: The
SGC-NLC formulation can significantly improve the absorption of GPS, which
provides an effective approach for enhancing the oral absorption of drugs.
Keywords: gypenosides,
nanostructured lipid carriers, bile salt, in vitro release,
bioavailability