108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

microRNA-944 通过直接靶向 IGF-1R 并使 PI3K/Akt 信号通路失活来抑制肝细胞癌的恶化
Authors Lv L, Wang X, Ma T
Received 28 December 2018
Accepted for publication 25 February 2019
Published 29 March 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2531—2543
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S199818
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Alexandra R. Fernandes
Purpose: Recent
studies have identified microRNA-944 (miR-944) as a cancer-related miRNA, but
its expression and precise functions in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain
unknown.
Patients and methods: miR-944
expression in HCC tissues and cell lines were detected by RT-qPCR. A series of
functional assays were utilized to examine the influence of miR-944 on the
malignant phenotypes of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. More importantly, the
associated mechanisms underlying the activity of miR-944 in HCC cells were
investigated using bioinformatics, luciferase reporter assays, RT-qPCR, and
western blot analysis.
Results: In this
study, we report for the first time, a significant downregulation of miR-944 in
HCC tissues and cell lines and the correlation between its downregulation and
malignant clinical parameters, including Edmondson-Steiner grade, TNM stage,
and venous infiltration. Low miR-944 expression predicted poorer overall
survival rate and disease-free survival rate in patients with HCC.
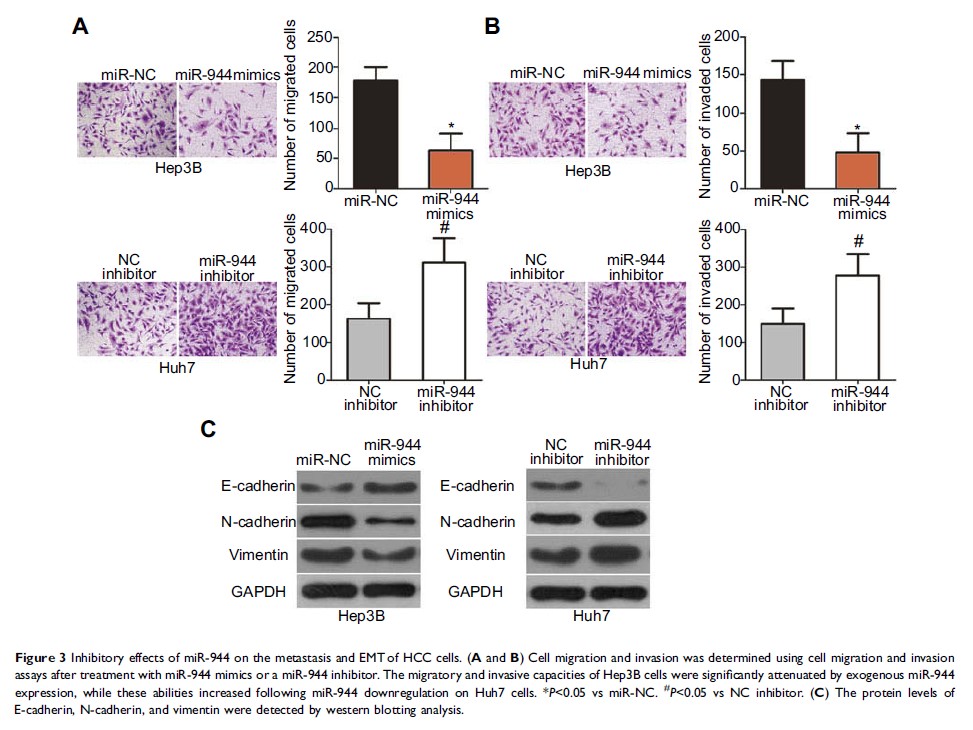
Functionally, exogenous miR-944 expression attenuated cell proliferation, clone
formation, metastasis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increased
apoptosis in HCC, whereas miR-944 knockdown produced the opposite results. In
addition, ectopic miR-944 expression hindered HCC tumor growth in vivo.
Mechanistically, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) was
demonstrated to be the direct target gene of miR-944 in HCC cells. Furthermore,
the expression level of miR-944 was inversely correlated with IGF-1R expression
in HCC tissues. Rescue experiments showed that IGF-1R was at least partially
responsible for the effects of miR-944 on the malignant phenotypes of HCC
cells. In addition, the PI3K/Akt pathway was notably deactivated, both in vitro
and in vivo, upon miR-944 upregulation.
Conclusion: This
study provides the first evidence that miR-944 directly targets IGF-1R and
inhibits the aggressiveness of HCC, in vitro and in vivo, by decreasing
PI3K/Akt signaling. Hence, targeting miR-944 may open a new avenue for the
treatment of patients with HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular
carcinoma, microRNA-944, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, PI3K/Akt
pathway, epithelial-mesenchymal transition