108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

原发性骨髓淋巴瘤的临床特征和预后因素
Authors Wang G, Chang Y, Wu X, Li X, Li L, Zhang L, Fu X, Sun Z, Zhang X, Zhang M
Received 14 September 2018
Accepted for publication 23 January 2019
Published 29 March 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2553—2563
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S187522
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background: Primary
bone marrow lymphoma (PBML) is a very uncommon neoplasm originally arising in
the bone marrow system, and the most common pathological type is diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma.
Patients and methods: To
describe the clinical characteristics of PBML and evaluate the risk factors
related to prognosis, we recruited and studied 66 patients from our center and
the current published literature. Various symptoms are present at the onset of
PBML, the most important of which is cytopenia, followed by fever. Forty-seven
of these patients were included in our analysis.
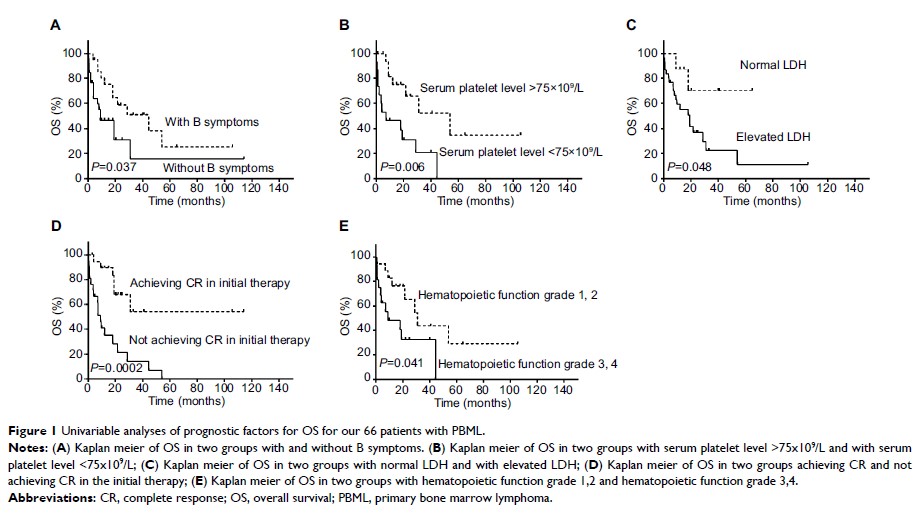
Results: Univariate
analysis suggested that B symptoms (P =0.024), a low serum platelet level (<75×109/L; P =0.032), an
elevated serum LDH level (P =0.039), and not achieving a complete response (CR)
following initial therapy (P =0.007) are associated with worse outcomes.
Multivariate analysis showed that only a low serum platelet level (<75×109/L), B
symptoms, and not achieving a CR following initial therapy are independent
factors for prognosis. In addition, intensive regimens appear to be beneficial
for prognosis.
Conclusion: PBML is a
lymphoma with special clinical features, and its recognition is important for
establishing a definitive prognosis model and searching for appropriate
therapy.
Keywords: diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma, primary bone marrow lymphoma, bone marrow, B symptoms,
cytopenia