9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

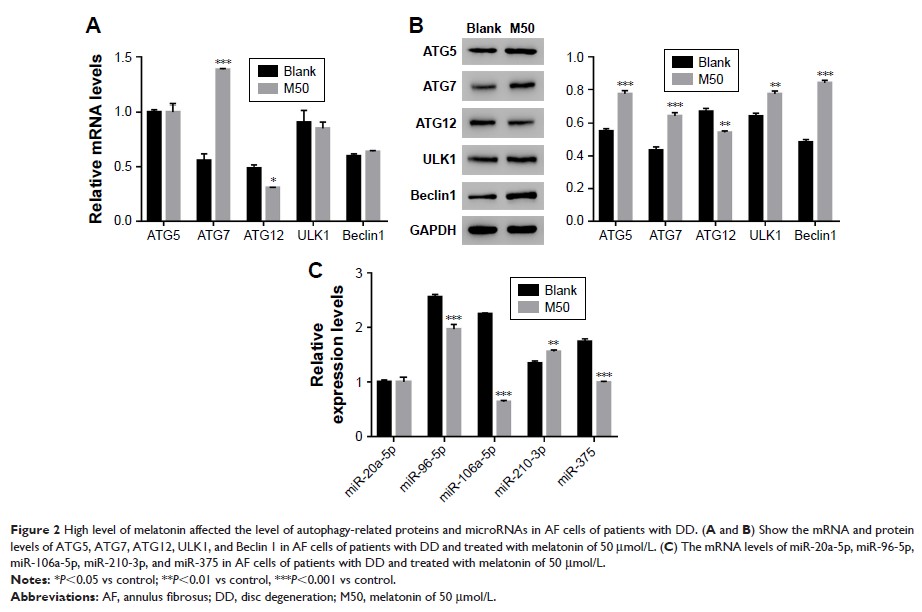
褪黑激素通过抑制 miR-106a-5p/ATG7 信号通路,有利于人体纤维环细胞的生长
Authors Hai B, Ma Y, Pan X, Yong L, Liang C, He G, Yang C, Zhu B, Liu X
Received 7 November 2018
Accepted for publication 18 February 2019
Published 28 March 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 621—630
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S193765
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Background: Disc
degeneration (DD) is one of the common diseases worldwide, which deeply
influences normal life and leads to excruciating pain. However, an effective
treatment for DD is still not identified.
Method: The
present study systemically examined the effect of melatonin on annulus fibrosus
(AF) cells of patients with DD.
Results: Melatonin
had the effect of promoting proliferation, inducing autophagy, and suppressing
apoptosis on AF cells of patients with DD. Moreover, melatonin contributed to
the translation and transcription of autophagy-related protein ATG7 and inhibited
the function of miR-106a-5p in AF cells. In addition, the results suggested
that miR-106a-5p mediated the expression of ATG7 by directly binding to its
3'UTR in AF cells.
Conclusion: This
research not only gained a deep insight of melatonin mode of action, but also
indicated its potential target signaling pathway in AF cells.
Keywords: disc
degeneration, melatonin, ATG7, miR-106a-5p