9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-664 的过表达与总体存活率较差有关,并加速肝细胞癌的细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Wang X, Zhou Z, Zhang T, Wang M, Xu R, Qin S, Zhang S
Received 25 September 2018
Accepted for publication 3 January 2019
Published 28 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2373—2381
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S188658
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Introduction: Hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death worldwide.
This study aimed to investigate the expression patterns of microRNA-664
(miR-664) in HCC tissues and cells, and assess its clinical significance and
functional role in HCC.
Patients and methods: One
hundred and thirty-four paired HCC and non-cancerous tissues were collected
from patients who underwent surgery in Qianfoshan Hospital affiliated to
Shandong University (Shandong, China) between 2009 and 2012. Expression of
miR-664 was measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
(qRT-PCR). Prognostic value of miR-664 in HCC was evaluated using Kaplan–Meier
survival analysis and Cox regression analysis. Cell proliferation was analyzed
using the CCK-8 assay, and cell migration and invasion of HCC cells was
evaluated by the Transwell assay.
Results: Expression
of miR-664 was significantly upregulated in HCC tissues and cells when compared
with the normal controls (all P <0.05). MiR-664 expression was associated with
lymph node metastasis, TNM stage and differentiation (all P <0.05) in the
HCC patients. High miR-664 expression predicted poor overall survival
(log-rank P =0.004)
and acted as an independent prognostic factor (HR =1.945, 95%
CI=1.078–3.508, P =0.027). According to cell experiments, the
upregulation of miR-664 could promote, whereas the downregulation of miR-664
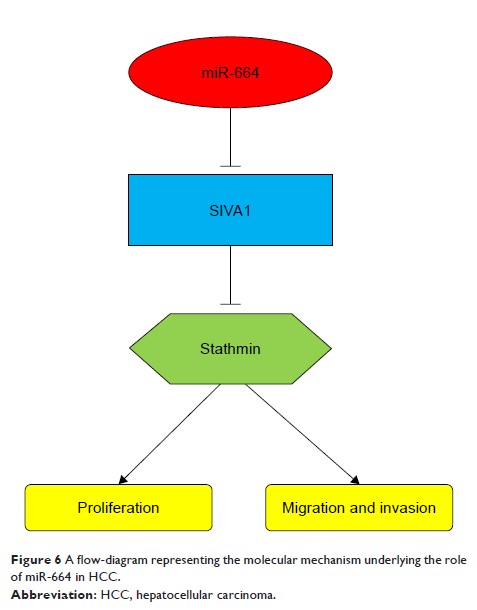
could inhibit proliferation, migration and invasion of HCC cells (all P <0.05). SIVA1
was predicted as a direct target gene of miR-664 in HCC.
Conclusion: All data
indicated that overexpression of miR-664 is associated with poor prognosis of
HCC patients, and may enhance tumor progression of HCC by targeting SIVA1.
MiR-664 may be a candidate therapeutic target for HCC treatment.
Keywords: MiR-664,
prognosis, proliferation, migration, invasion, hepatocellular carcinoma, tumor
progression