9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

SIRT4 通过抑制谷氨酰胺代谢抑制甲状腺癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭能力
Authors Chen Z, Lin J, Feng S, Chen X, Huang H, Wang C, Yu Y, He Y, Han S, Zheng L, Huang G
Received 2 October 2018
Accepted for publication 4 February 2019
Published 28 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2397—2408
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S189536
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: SIRT4, a
protein localized in the mitochondria, is one of the least characteristic
members of the sirtuin family. It is known that SIRT4 has deacetylase activity
and plays a role in energy metabolism, but little is known about its possible
role in carcinogenesis. Recently, several studies have suggested that SIRT4 may
function as either a tumor oncogene or a tumor suppressor gene. However, its
relationship with thyroid cancer remains unclear.
Methods: We stably
overexpressed SIRT4 or silenced its expression in the human thyroid cancer cell
line BCPAP by means of lentiviral vectors. We conducted a variety of tests,
such as CCK-8, wound healing, migration, and invasion assays, to investigate
the role of SIRT4 in the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of
thyroid cancer cells. We also investigated the effects of SIRT4 overexpression
on cell cycle progression and apoptosis of BCPAP cells and studied the role of
glutamine metabolism in the effects of SIRT4 on BCPAP cell migration and invasion.
Finally, we analyzed SIRT4 expression levels in thyroid cancer specimens by
immunohistochemistry and investigated their association with
clinicopathological features.
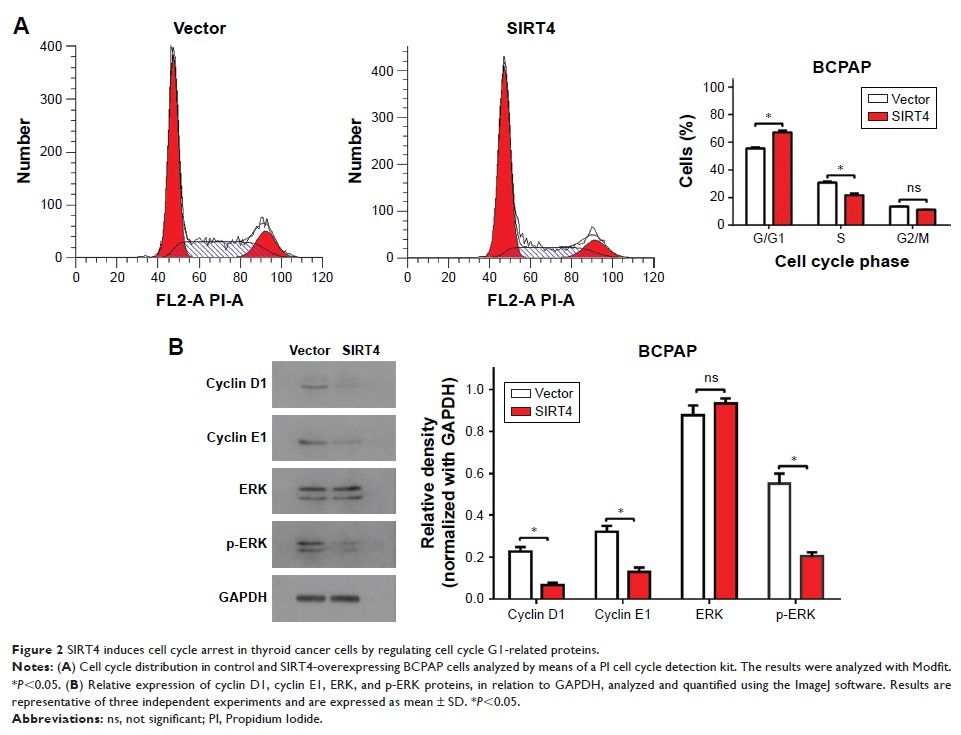
Results: Overexpression
of SIRT4 inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of
BCPAP thyroid cancer cells, blocked the cell cycle in the G0/G1 phase, and
induced apoptosis. Mechanistically, SIRT4 inhibited BCPAP migration and
invasion by inhibiting glutamine metabolism. Moreover, we found that SIRT4
protein levels in thyroid cancer tissues were markedly lower than in their
non-neoplastic tissue counterparts (P <0.001).
Conclusion: SIRT4
plays a pivotal role in the growth and metastasis of thyroid cancer cells and
could be a potential therapeutic target in thyroid cancer.
Keywords: SIRT4,
thyroid cancer, proliferation, migration, invasion, glutamine