9 9 6 5 3
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

木犀草素通过胶质瘤中 MAPK 活化诱导细胞凋亡和自噬,以抑制肿瘤增殖
Authors You Y, Wang R, Shao N, Zhi F, Yang Y
Received 17 October 2018
Accepted for publication 4 February 2019
Published 28 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2383—2396
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S191158
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Purpose: Glioma is
a malignant tumor that originates in the brain and spine and is difficult to be
completely removed. Though glioma patients receive active treatment, the
survival rate is still poor. Therefore, it is urgent to discover a new medicine
to treat glioma patients in order to improve the survival rate. In this study,
we explored the anticancer effect and the potential mechanism of luteolin on
glioma in vitro.
Materials and methods: Cell
viability was determined by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Fluorescent
microscopy and flow cytometry analysis were used to determine the cellular
apoptosis. Western blot analysis was performed to explore the changes in
protein expression. Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis
was utilized to evaluate the expression level of the tumor suppressor
miR-124-3p.
Results: CCK-8
assays indicated that luteolin significantly inhibited glioma cell
proliferation in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Fluorescent microscopy and
flow cytometry analysis confirmed that luteolin induced glioma cell apoptosis.
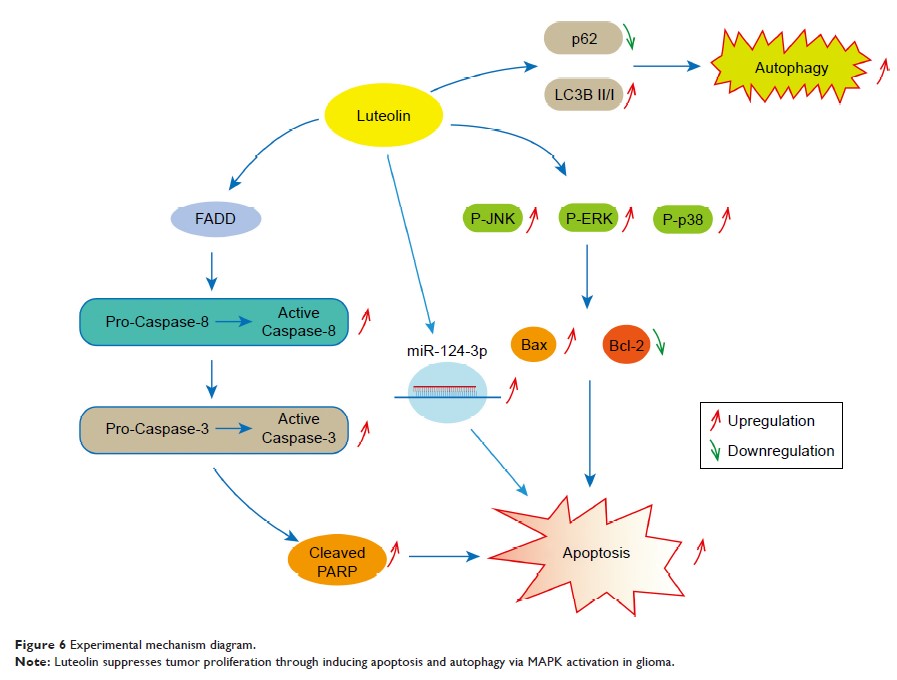
Western blot analysis showed that luteolin induced cellular apoptosis in glioma
cells via MAPK activation (JNK, ERK, and p38). Luteolin stimulated the death
receptor (FADD) to regulate the apoptosis proteins (Caspase-8, Caspase-3, and
PARP). Luteolin increased the expression levels of LC3B II/I and downregulated
the level of p62 that promotes cell autophagy. Finally, qRT-PCR confirmed that
luteolin upregulated the expression levels of miR-124-3p.
Conclusion: These
findings illustrate that luteolin may be a potential drug for glioma treatment.
Keywords: glioma,
luteolin, apoptosis, autophagy, miR-124-3p