9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

负载补骨脂素的脂质 - 聚合物杂化纳米粒增强阿霉素对多药耐药 HepG2 细胞的功效
Authors Yuan Y, Cai T, Callaghan R, Li Q, Huang Y, Wang B, Huang Q, Du M, Ma Q, Chiba P, Cai Y
Received 6 October 2018
Accepted for publication 7 January 2019
Published 27 March 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 2207—2218
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S189924
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Psoralen
(PSO), a major active component of Psoralea corylifolia, has been shown to
overcome multidrug resistance in cancer. A drug carrier comprising a
lipid-monolayer shell and a biodegradable polymer core for sustained delivery
and improved efficacy of drug have exhibited great potential in efficient
treatment of cancers.
Methods: The
PSO-loaded lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles were prepared and characterized.
In vitro cytotoxicity assay, cellular uptake, cell cycle analysis, detection of
ROS level and mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and western blot were
performed.
Results: The
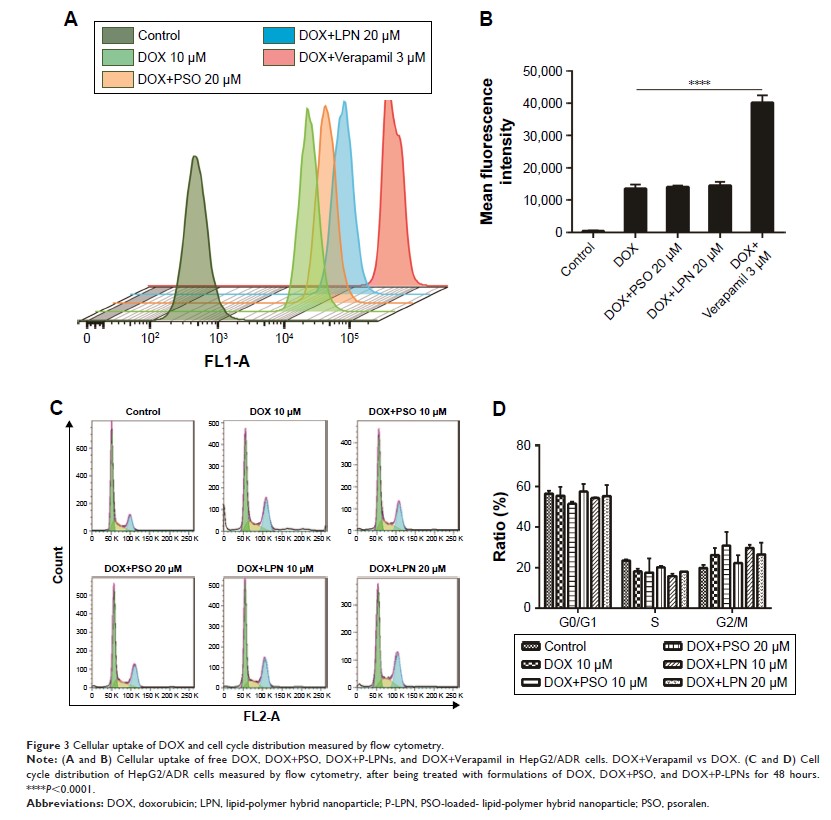
P-LPNs enhanced the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin (DOX) 17-fold compared to free
DOX in multidrug resistant HepG2/ADR cells. Moreover, P-LPNs displayed
pro-apoptotic activity, increased levels of ROS and depolarization of ΔΨm. In
addition, there were no significant effects on cellular uptake of DOX, cell
cycle arrest, or the expression of P-glycoprotein. Mechanistic studies
suggested that P-LPNs enhanced DOX cytotoxicity by increased release of
cytochrome c and enhanced caspase3 cleavage, causing apoptosis in HepG2/ADR
cells.
Conclusion: The
lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles can be considered a powerful and promising
drug delivery system for effective cancer chemotherapy.
Keywords: lipid-polymer
hybrid nanoparticles, psoralen, drug delivery, HepG2, ADR cells, apoptosis