9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

LAPTM4B 促进肿瘤生长并诱导肝细胞癌自噬
Authors Wang F, Wu H, Zhang S, Lu J, Lu Y, Zhan P, Fang Q, Wang F, Zhang X, Xie C, Yin Z
Received 10 January 2019
Accepted for publication 5 March 2019
Published 27 March 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2485—2497
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S201092
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Background: Hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most frequent cancers and the third leading cause
of cancer-related deaths. It has been reported that lysosomal associated
transmembrane protein LAPTM4B expression is significantly upregulated in human
cancers and closely associated with tumor initiation and progression.
Purpose: We aimed
to reveal the relevance of LAPTM4B and the pathogenesis of HCC. Methods: Cell
viability assessment, colony formation assay, in vivo xenograrft model,
microarray, real-time PCR, immunofluorescence and western blot analysis were
applied.
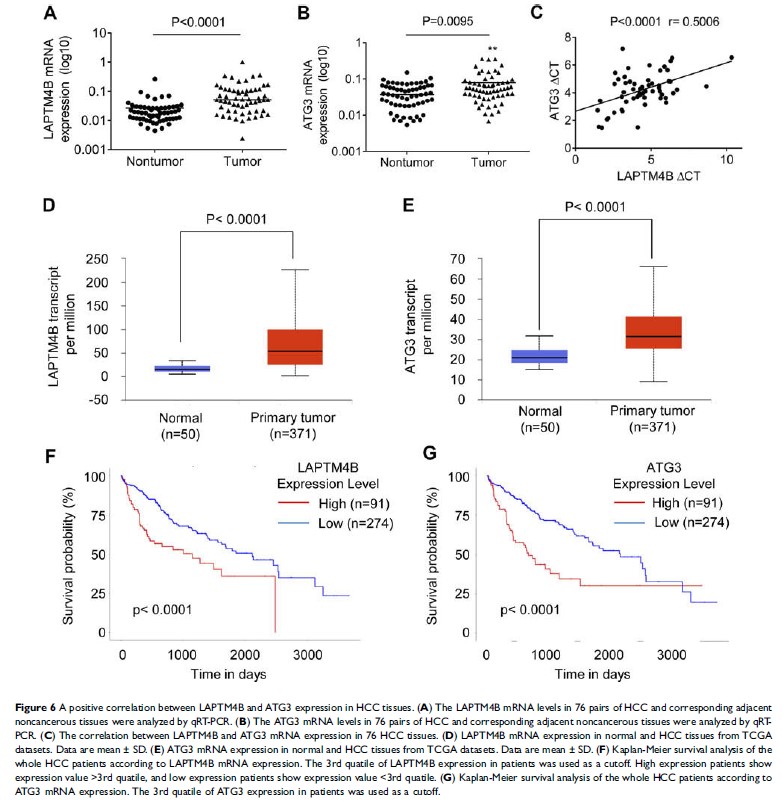
Results: Our
results demonstrated that LAPTM4B promoted HCC cell proliferation in vitro and
tumorigenesis in vivo . Additionally, upon starvation conditions,
LAPTM4B facilitated cell survival, inhibited apoptosis and induced autophagic
flux. Expression profiling coupled with gene ontology (GO) analysis revealed
that 159 gene downregulated by LAPTM4B silencing was significantly enriched in
response to nutrient and some metabolic processes. Moreover, LAPTM4B activated
ATG3 transcription to modulate HCC cell apoptosis and autophagy.
Conclusion: Our
findings demonstrate that LAPTM4B acts as an oncogene that promotes HCC
tumorigenesis and autophagy, and indicate that LAPTM4B may be used as a novel
therapeutic target for HCC treatment.
Keywords: autophagy,
apoptosis, LAPTM4B, ATG3