9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

WFDC2 通过激活 AKT 信号通路和对 MMP-2 表达进行调节来促进上皮 - 间质转化(EMT)
Authors Chen Y, Huang L, Wang S, Li JL, Li M, Wu Y, Liu T
Received 31 October 2018
Accepted for publication 31 January 2019
Published 27 March 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2415—2424
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S192950
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objective: To
understand the role of WFDC2 in metastasis of ovarian cancer.
Methods: By
knockdown or overexpression of WFDC2 , we demonstrated the role of WFDC2 in
epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT).
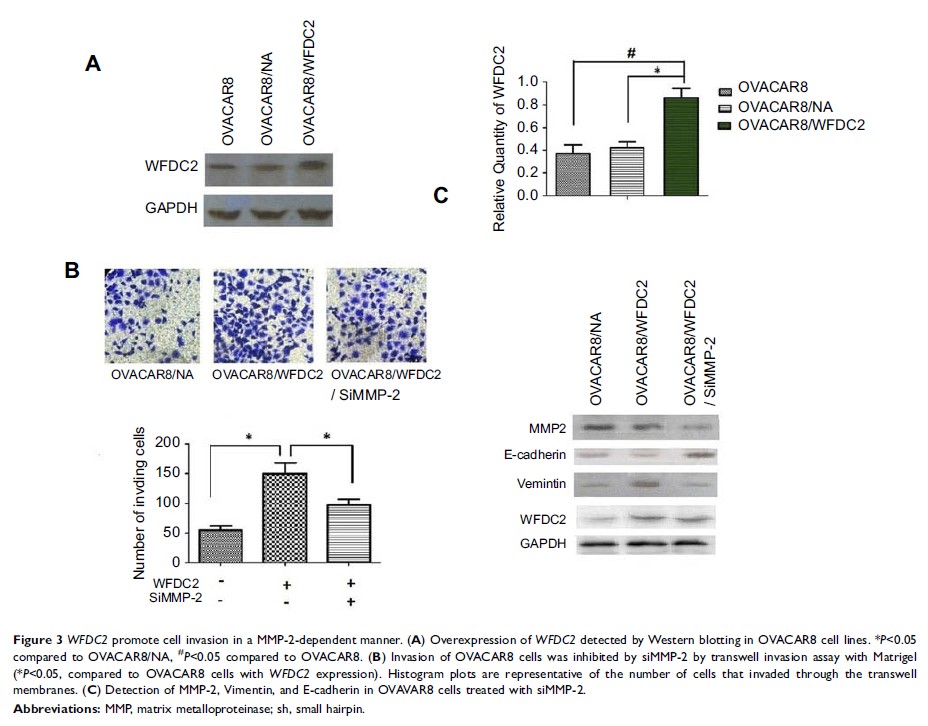
Results: We
demonstrated that stable knockdown of WFDC2 suppressed EMT along with the upregulation
of E-cadherin and the downregulation of Vimentin. In addition, WFDC2 knockdown
decreases matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) expression in in vitro cell model
and in in vivo nude mice xenografts. The correlation of WFDC2 and
MMP-2 expression in the clinical sample confirmed that WFDC2 was
tightly correlated with the development of tumor. More importantly, the EMT
phenotype and cell invasion induced by WFDC2 overexpressing can be reversed by the
siMMP-2 and P13K/AKT signaling inhibitor.
Conclusion: WFDC2 contributed
to ovarian cancer metastasis and EMT as a positive regulator by activating AKT
signaling pathway and inducing MMP-2 expression.
Keywords: WFCD2,
ovarian cancer, metastasis, cell migration and invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal
transition