9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

Th9/IL-9 对裸鼠胃癌生长的影响
Authors Cai L, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Chen H, Hu J
Received 11 December 2018
Accepted for publication 5 February 2019
Published 26 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2225—2234
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S197816
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Objective: By
neutralizing IL-9 in a nude mouse model, the study aimed to investigate the
role of Th9/IL-9 on the growth of gastric cancer in mice.
Materials and methods: Male
BALB/c nude mice were randomly divided into three groups: a normal control
group (Control), an SGC-7901 xenografted nude mice model group (Model), and a
rIL-9 treatment group (Treat). The weight of the tumors was recorded to
calculate the tumor inhibition rate. Flow cytometry was used to detect the cell
frequency of Th9, Th17, and Treg in peripheral blood. The IL-4, IL-9, IL-10,
IL-25, VEGF, and TGF-β levels in serum were determined by ELISA. The cellular
migration and invasion were investigated by transwell assay.
Immunohistochemical and Western blot were used to detect the expression of
IL-9, CD34, PU.1, p53, and p21 proteins in gastric cancer tissue. The mRNA
expression levels of IL-9, IL-21, and PU.1 in gastric cancer tissue were
determined by qRT-PCR.
Result: rIL-9 can
significantly inhibit the growth of gastric cancer. The frequency of Th9, Th17,
and Treg in peripheral blood was decreased upon treatment. The levels of IL-4,
IL-9, IL-10, IL-25, VEGF, and TGF-β in serum were significantly reduced in the
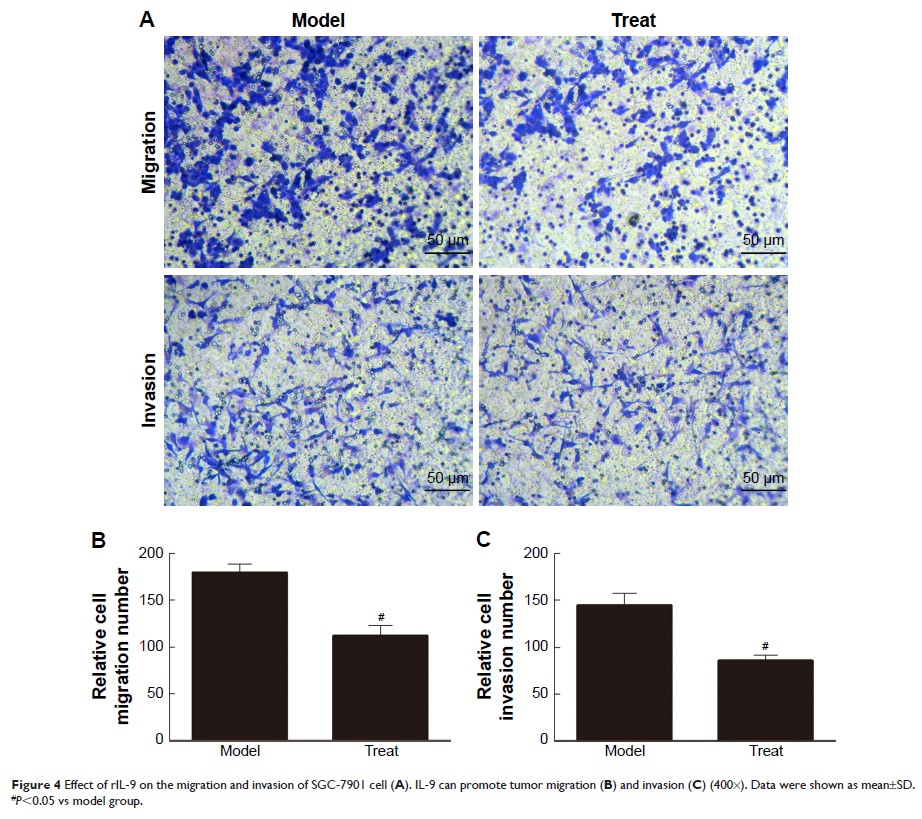
Treat group compared with the Model group (P <0.05). rIL-9 can inhibit cellular migration and
invasion and reduce the mRNA level of IL-9, IL-21, and PU.1. Meanwhile, in the
Treat group, the expression of IL-9, CD34, and PU.1 was significantly reduced,
whereas the expression of p53 and p21 was significantly increased compared with
the Model group (P <0.05).
Conclusion: This
study suggested that Th9/IL-9 has a deleterious role in gastric cancer.
Keywords: Th9,
IL-9, gastric cancer, CD4 T lymphocyte