9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

诱导化疗和放疗之间的间隔对鼻咽癌患者生存率的影响
Authors Yang S, Fu X, Huang G, Chen J, Luo S, Wang Z, Kong F, Wu G, Lin S, Wang F, Chen L
Received 22 November 2018
Accepted for publication 29 January 2019
Published 22 March 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2313—2320
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S195559
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Background: There
have been no reliable scientific studies examining whether the interval between
induction chemotherapy (IC) and initiating radiotherapy is associated with poor
outcomes of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
Patients and methods: In this
retrospective study, we included a total of 239 local advanced NPC patients who
underwent concurrent chemoradiotherapy and IC. Based on the interval between IC
and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), the patients were classified
into three groups as follows: Group A (≤7 vs >7 days), Group B (≤14 vs
>14 days), and Group C (≤ 21 vs >21 days). Univariate and multivariate
regression analyses were performed to determine the prognostic factors of
survival outcomes. The differences between the two groups were compared by the
log-rank test.
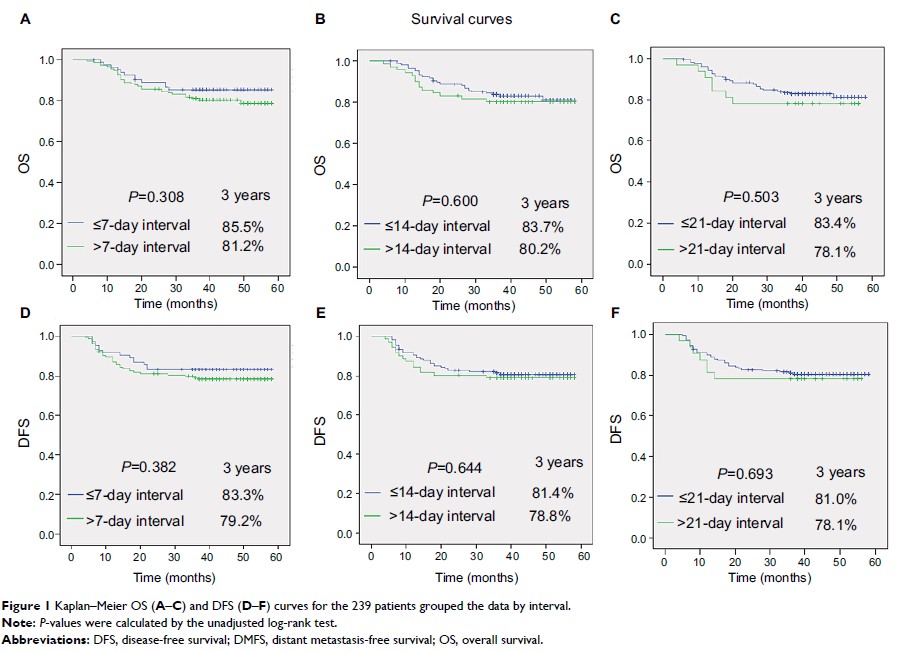
Results: The
median IC-IMRT interval was 9 days (range, 1–76 days). The median follow-up
time was 40 months (range, 4–58 months). The IC-IMRT interval including Group
A, Group B, and Group C was not significantly associated with overall survival
(OS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), locoregional relapse-free
survival (LRFS), or disease-free survival (DFS). Multivariate analysis showed
that the tumor stage was the independent significant predictor for OS, DMFS,
LRFS, and DFS. But it appears that there was a trend toward improvement in the
outcome of ≤7 days group in OS from the Kaplan–Meier curves.
Conclusion: It is
also feasible to postpone radiotherapy for 1–3 weeks if patients were unable to
receive treatment immediately due to chemotherapy complications such as bone
marrow suppression. However, we suggest that patients should start IMRT as soon
as possible after IC.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal
carcinoma, interval, induction chemotherapy, radiotherapy