108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ZNF804A 遗传变异对脑结构的多效作用:磁共振成像研究的综合分析
Authors Wang S, He Y, Chen Z, Li Y, Zhao J, Lyu L
Received 20 May 2018
Accepted for publication 3 October 2018
Published 21 March 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 721—729
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S174728
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Objective: The zinc
finger protein 804A (ZNF804A ) gene encodes the protein 804A containing the
C2H2 zinc finger structure, which plays an important role in embryonic nerve
development and repair. Previous studies have shown a significant association
between the ZNF804A genetic variation polymorphism rs1344706
and the risk of schizophrenia and brain structure abnormalities. However, the
findings are inconsistent.
Materials and methods: Seventeen
studies on structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI), with 1,031
schizophrenia patients and 3,416 healthy controls, were included in the
meta-analysis. These analyses were performed using Anisotropic Effect-Size
Signed Differential Mapping (AES-SDM) software and Comprehensive Meta-Analysis
(CMA) software.
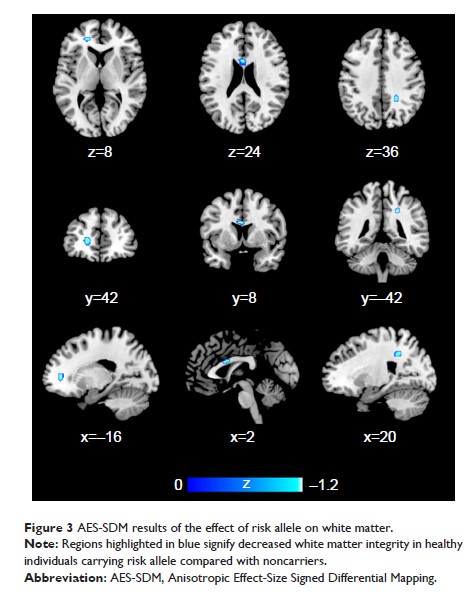
Results: rs1344706
risk allele carriers of schizophrenia had increased gray matter in the brain
regions including frontal lobe, temporal lobe, and other brain regions, but the
carriers of healthy individuals had decreased gray matter and white matter
integrity in the frontal lobe, central network, and other brain regions. The
results of sensitivity analysis are stable, but publication bias exists in a
few analyses of indexes.
Conclusion: Abnormalities
of brain structure have a strong relationship with ZNF804A gene
rs1344706 polymorphism, but the association may be different in healthy
individuals and those with mental disorders.
Keywords: ZNF804A,
genetic variation, magnetic resonance imaging, brain structure, meta-analysis