108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

核自身抗原精子蛋白升高通过诱导细胞增殖来促进黑素瘤进展
Authors Li JX, Wei CY, Cao SG, Xia MW
Received 11 December 2018
Accepted for publication 14 February 2019
Published 21 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2105—2113
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S197813
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
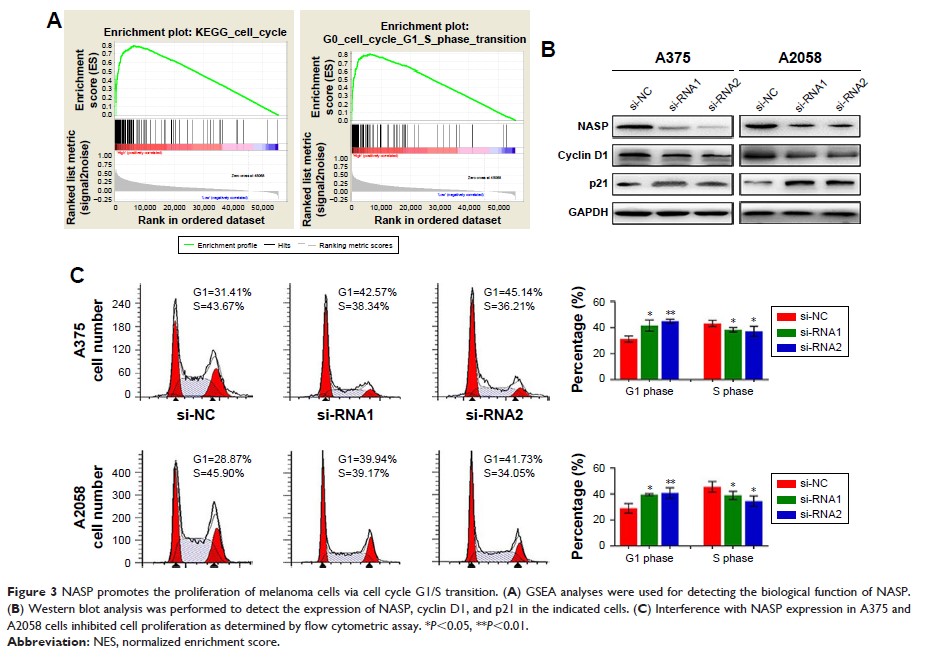
Background: Nuclear
auto-antigenic sperm protein (NASP) has been implicated in tumorigenesis.
However, its role in melanoma is still unclear.
Materials and methods: In the
present study, we detected the mRNA and protein level of NASP in melanoma cell
lines and tissues. Then the role of NASP was investigated by transfecting with
NASP siRNAs. Finally, the prognosis of NASP was analyzed in 100 melanoma
patients through Cox regression and Kaplan–Meier analyses.
Results: We showed
that NASP was significantly overexpressed in melanoma tissues, and unregulated
NASP promoted melanoma cell proliferation via promoting cell cycle G1/S phase
transition. Additionally, the expression of NASP was closely related to
proliferating cell nuclear antigen, a widely accepted biomarker for cell
proliferation. Clinically, we found that a high level of NASP predicated poor
overall survival and high cumulative recurrence rates. Multivariate analysis
revealed that NASP was a risk biomarker for predicting the prognosis of
melanoma patients.
Conclusion: Elevated
NASP plays an important role in melanoma cell proliferation and tumor
progression, and it can be used as an independent prognostic biomarker for
melanoma patients.
Keywords: NASP,
melanoma, proliferation, prognosis