9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

胸腔引流液对肺癌细胞增殖、迁移、凋亡及耐药性的影响
Authors Mao Y, Yu Y, Han Y
Received 10 September 2018
Accepted for publication 1 February 2019
Published 20 March 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2253—2259
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S187019
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
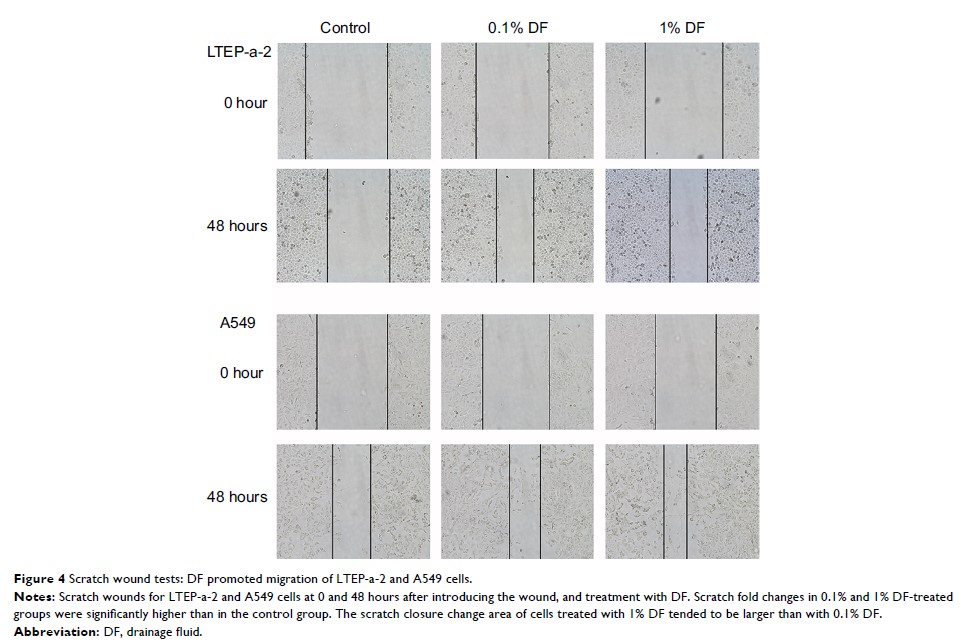
Background: This
study aimed to clarify the effect of thoracic drainage fluid (DF) on lung
cancer cells in vitro.
Methods: We
assessed the influence of DF on the proliferation and migration of lung cancer
cells (LTEP-a-2 and A549) using the MTT cell proliferation assay and scratch
wound assay. Cell apoptosis was determined by flow cytometric analysis. We also
investigated the effect of DF on drug chemosensitivity, assessing viability of
LTEP-a-2 and A549 cells.
Results: The
proliferative rates of cancer cells in the DF-treated group were significantly
higher than those of the control group. Similar results were obtained for cell
migration of lung cancer cells. Cells in the DF-treated groups showed a lower
percentage of apoptosis than those of the control groups. Chemosensitivity of
lung cancer cells to doxycycline and cisplatin (DDP) was lowered by DF.
Conclusion: These
findings suggest that DF affects lung cancer cells by promoting proliferation
and migration, inhibiting apoptosis, and increasing drug resistance.
Keywords: lung
cancer, drainage fluid, proliferation and migration, apoptosis, drug resistance