108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

产生 KPC-2 的高毒力肺炎克雷伯菌在中国东部导致脑膜炎的高患病率
Authors Xu M, Fu Y, Fang Y, Xu H, Kong H, Liu Y, Chen Y, Li L
Received 23 October 2018
Accepted for publication 25 January 2019
Published 18 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 641—653
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S191892
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Background: Klebsiella pneumoniae has
been the leading causative pathogen for adult bacterial meningitis in several
Asian countries. The clinical and microbiological characteristics of K. pneumoniae meningitis
in mainland China are still unknown.
Materials and methods: The
clinical data of patients with K. pneumoniae meningitis from January 2011 to
July 2017 in a tertiary hospital were retrospectively evaluated. The isolates
were tested for antibiotic-resistance genes, virulence-associated genes, and
molecular subtypes. Hypervirulent K. pneumoniae (hvKP) was defined as the presence
of pLVPK-like virulence plasmid.
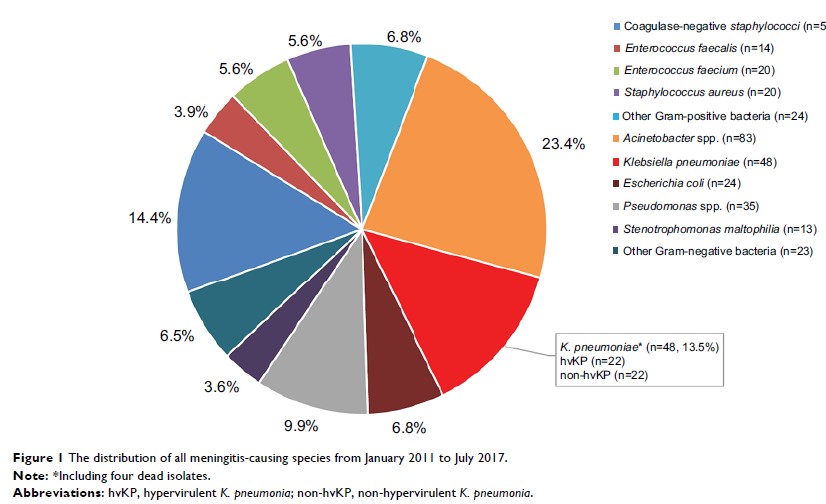
Results: During
the study period, a total of 48 patients with meningitis caused by K. pneumoniae were
identified, accounting for 21.2% (48/226) of Gram-negative bacilli meningitis.
Of the 44 available isolates, 65.9% (29/44) were carbapenem resistant, and all
except one harbored bla KPC-2. K64 was the
most common serotype (n=13), followed by K47 (n=11) and K1 (n=5). The
pLVPK-related genetic loci were found in about half of isolates (iutA : 56.8%, iucA : 56.8%, rmpA2 :50.0%, rmpA : 43.2%,
and iroN :
40.9%). Twenty-two strains carrying pLVPK-derived virulence plasmid were
defined as hvKP. Notably, the coexistence of bla KPC-2-encoding
plasmid and the pLVPK-derived virulence plasmid was detected in 15 strains
(34.1%, 15/44), suggesting K. pneumoniae carbapenemase-2 (KPC-2)-producing hvKP.
The proportion of KPC-2-producing hvKP by year increased remarkably from 0%
(2011) to 71.4% (2017). Of the 15 KPC-2-producing hvKP strains, 80.0% (12/15)
were assigned to sequence type 11 and 2 strains (13.3%) belonged to clonal
complex 23. Most of the patients infected with KPC-2-producing hvKP had
preceding postneurosurgical state (93.3%, 14/15) and severe pneumonia (73.3%,
11/15). All the cases (100%, 15/15) had fatal outcome.
Conclusion: The high
prevalence and mortality of K. pneumoniae , especially KPC-2-producing hvKP
meningitis, in China should be of concern. The implementation of
epidemiological surveillance and identification of an effective clinical
treatment are paramount.
Keywords: meningitis,
hypervirulent K. pneumonia , bla KPC-2, rmpA2 , pLVPK-like
virulence plasmid