108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

TMED2 的表达增加是乳腺癌患者的不利预后因素
Authors Lin X, Liu J, Hu SF, Hu X
Received 31 October 2018
Accepted for publication 19 February 2019
Published 18 March 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2203—2214
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S192949
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: We
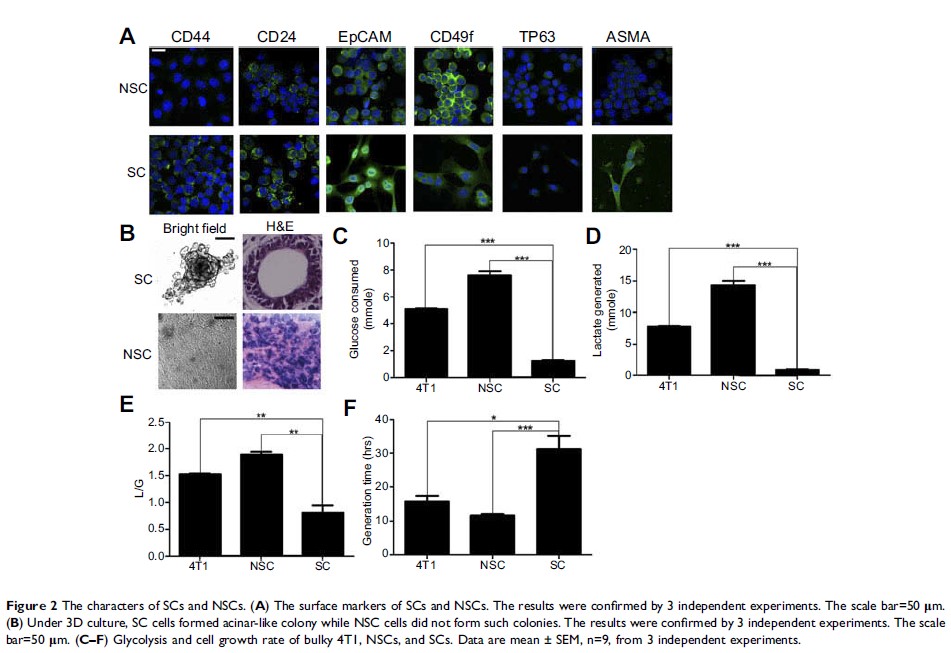
obtained 2 types of clones which were termed SC (sphere-shaped clone) and NSC (non-sphere-shaped
clone) from 4T1 cells by monoclonal culture. SC and NSC were distinct in
morphology, surface marker, metabolism and proliferation rate. With the
transcriptome sequencing data analysis, we found TMED2 expressed
higher in SCs. TMED2 was a member of the transmembrane emp24 domain and might
play roles in cancer cell proliferation. However, its prognostic roles in
breast cancer remained unknown. We aimed to investigate the prognostic values
of TMED2 in patients with breast cancer.
Methods: We used
UALCAN (http://ualcan.path.uab.edu) and the Human Protein Atlas
(www.proteinatlas.org) to explore the TMED2 expression level and DNA
methylation data between breast cancer and normal breast tissue. With Oncomine
(www.oncomine.org), we investigated the copy number of TMED2 in
breast cancer sample and normal breast tissue. We used the Kaplan–Meier Plotter
database (http://kmplot.com/analysis) to analyze prognostic values of TMED2 mRNA
expression in all breast cancers and in different intrinsic subtypes. Moreover,
protein expression levels of TMED2 were confirmed by Western blot in breast
cancer tissues and normal mammary tissue as well as SCs and NSCs.
Results: TMED2
significantly upregulated in breast cancer patients compared to normal mammary
samples. Meanwhile, the increased expression of TMED2 mRNA was
closely associated with reduced overall survival (OS) in all breast cancers,
and with reduced OS in patients with ER-positive, Luminal A or Luminal B breast
cancer subtypes. Moreover, western blot confirmed that TMED2 increased
expressed was correlated with the reduced OS at protein levels.
Conclusion: Increased
expression of TMED2 was significantly related to unfavorable outcomes in
patients with breast cancer. Thus, we supposed TMED2 is oncogenic and a potential
target for breast cancer therapy and these preliminary findings require further
study to determine whether TMED2-targeting reagents might be developed for
clinical application in breast cancer.
Keywords: breast
cancer, SC, NSC, TMED2, overall survival, KM plotter