108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

围手术期服用右美托咪定对老年患者心脏手术后谵妄的影响:一项双盲、多中心、随机研究
Authors Shi CX, Jin J, Qiao LY, Li T, Ma JH, Ma ZK
Received 13 November 2018
Accepted for publication 26 January 2019
Published 15 March 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 571—575
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S194476
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Objective: Postoperative
delirium (POD) is a serious complication in elderly patients undergoing cardiac
surgery. This study was aimed at investigating the effect of perioperative
administration of dexmedetomidine for general anesthesia maintenance on
occurrence and duration of POD in elderly patients after cardiac surgery.
Methods: One
hundred and sixty-four patients were enrolled after cardiac surgery between
June 2009 and December 2016. Patients were assigned by a computer-generated
randomization sequence in a 1:1 ratio to receive dexmedetomidine general
anesthesia maintenance or propofol general anesthesia maintenance. POD was
assessed every day with confusion assessment method for intensive care units
(ICU) during the first 5 postoperative days.
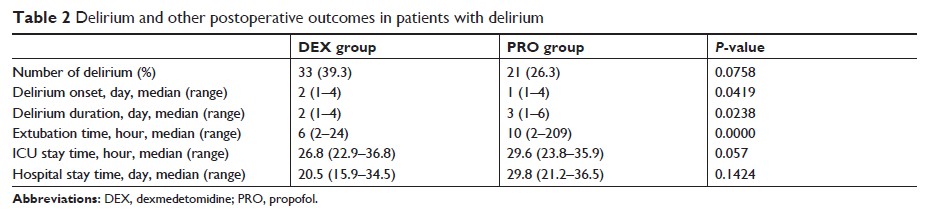
Results: There was
no significance in incidence of POD between the dexmedetomidine group and the
propofol group (P =0.0758).
In patients treated with dexmedetomidine, the median onset time of delirium was
delayed (second day vs first day) and the duration of delirium reduced (2 days
vs 3 days) when compared with propofol-treated patients. The
dexmedetomidine-treated patients also displayed a lower VAS score and less
opiate analgesic consumption. No difference was observed in respect to other
postoperative outcomes.
Conclusion: For
elderly patients, perioperative administration of dexmedetomidine reduced
incidence, delayed onset and shortened duration of POD after cardiac surgery.
Keywords: dexmedetomidine,
postoperative delirium, anesthesia, cardiac surgery, elderly patients