9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

利用黄连进行植物介导的银纳米粒子生物合成、表征和抗癌作用
Authors Pei J, Fu B, Jiang L, Sun T
Received 20 September 2018
Accepted for publication 13 December 2018
Published 15 March 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1969—1978
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S188235
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Tremendous
growth in nanotechnology has opened up new frontiers in fundamental and applied
aspects, including the synthesis of nanoscale matter and
understanding/utilizing its exotic physicochemical and optoelectronic
properties. Green-synthesis methods employing either biological microorganisms
or plant extracts have emerged as a simple and alternative to chemical
synthesis.
Methods: In our
present study, we aimed to synthesize silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in
combination with an aqueous extract of Coptis chinensis (CC) using a suitable
ecofriendly green-synthesis way.
Results: In our
results, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy revealed a near-absorbance peak at
450 nm, which confirmed the AgNP synthesis. The crystalline nature of the AgNPs
was revealed with X-ray diffraction. Transmission electron-microscopy analysis
showed spherically dispersed nanoparticles of 6–45 nm diameter. We analyzed the
elementary mechanism across A549 lung carcinoma cells ahead of treatment with
doses of CC-AgNPs (10 µg/mL and 25 µg/mL). The antiproliferative effect of
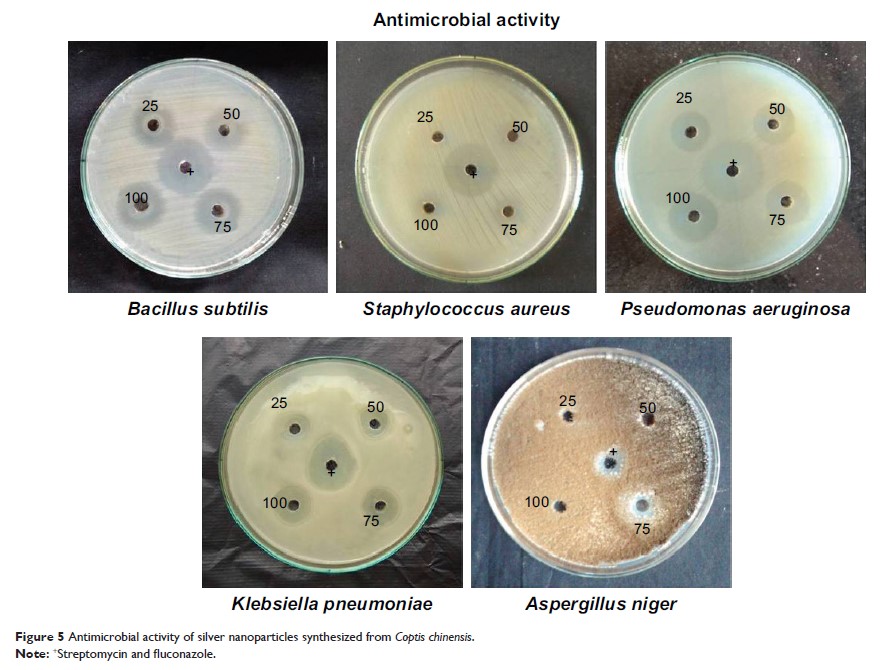
CC-AgNPs revealed a significant decline in cell viability. Antibacterial assays
with both Gram-negative (Escherichia coli ) and Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus )
bacteria exhibited a higher zone of inhibition against S. aureus .
Conclusion: Furthermore,
CC-AgNPs regulated apoptosis using the intrinsic pathway to inhibit A549-cell
proliferation. Proliferation migration and invasion were notably inhibited by
CC-AgNPs, which promoted apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating
the apoptotic pathway.
Keywords: Coptis chinensis ,
silver nanoparticles, antimicrobial, lung cancer, apoptosis, invasion