9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

载脂蛋白 B 升高可预测肝细胞癌患者的术后预后不良
Authors Yan X, Yao M, Wen X, Zhu Y, Zhao E, Qian X, Chen X, Lu W, Lv Q, Zhang L, Lu F
Received 29 October 2018
Accepted for publication 25 January 2019
Published 12 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1957—1964
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S192631
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Aims: To date,
curative resection remains to be the most optimal therapeutic choice of
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), though the overall survival (OS) remains
extremely unsatisfactory. To better manage the HCC patients, we evaluated the
prognosis predicting values of apolipoprotein B (ApoB) and low-density
lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) on the long-time survival of patients who
underwent surgical treatment in this study.
Methods: A
subgroup of 164 patients from our previously described follow-up cohort were
enrolled in this study, of whom the pre-surgery ApoB and LDL-C measurements
were available. They had been followed until January 2017, with a 19.5 months
median survival time. The prognosis predicting values of serum ApoB, LDL-C, and
other clinical variables were evaluated through Cox univariate and multivariate
analyses, meanwhile, Kaplan–Meier analysis was conducted to obtain the OS
curves.
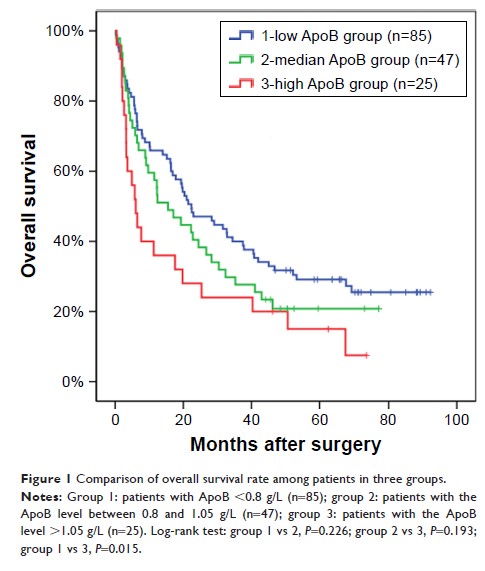
Results: Pre-surgery
ApoB was an independent prognosis predicting factor with HR as 1.396 (P =0.033), elevated
ApoB was associated with worse postsurgery prognosis in HCC patients.
Concordantly, Spearman’s correlation analysis revealed that value of
pre-surgery ApoB was to some extent correlated with tumor size (r =0.355, P <0.001). In
line with this, further univariate and multivariate logistic regression
analysis revealed that patients with higher ApoB value were more likely to have
larger tumor size (≥5 cm), with the OR value as high as 2.221 (95% CI:
1.288–3.830, P =0.004). Additionally, level of ApoB was found to be
highly correlated with the serum level of LDL-C (r =0.686, P <0.001).
Conclusion: ApoB
could be a valuable novel prognosis predicting marker for HCC patients who
underwent curative liver resection. Moreover, elevated ApoB level could
indicate worse outcome in HCC patients, which could be explained by the
relationship between ApoB and residual liver function.
Keywords: hepatocellular
carcinoma, curative resection, survival, apolipoprotein B