9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

他克莫司在狼疮性肾炎患者诱导治疗中的疗效和安全性
Authors Zhou TB, Lin SJ, Yang S, Lin WS
Received 29 September 2018
Accepted for publication 5 February 2019
Published 12 March 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 857—869
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S189156
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Background: The
purpose of this study was to detect the efficacy and safety of tacrolimus (TAC)
in induction therapy of patients with lupus nephritis.
Methods: Associated
studies were extracted from the PubMed and the Cochrane Library on July 10,
2018, and applicable investigations were pooled and analyzed by meta-analysis.
Data on complete remission (CR), total remission (TR; complete plus partial
remission), proteinuria levels, urine erythrocyte number, albumin, glomerular
filtration rate, negative rate of ds-DNA, C3 levels, C4 levels,
systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index (SLE-DAI), etc, were
extracted and pooled using RevMan 5.3.
Results: In the
therapeutic regimen of TAC + glucocorticoids (GC) vs cyclophosphamide (CYC) +
GC, the results indicated that the TAC group had high values of CR, TR,
albumin, and negative rate of ds-DNA, and low values of proteinuria levels and
SLE-DAI when compared with those in CYC group (all P <0.05). In the
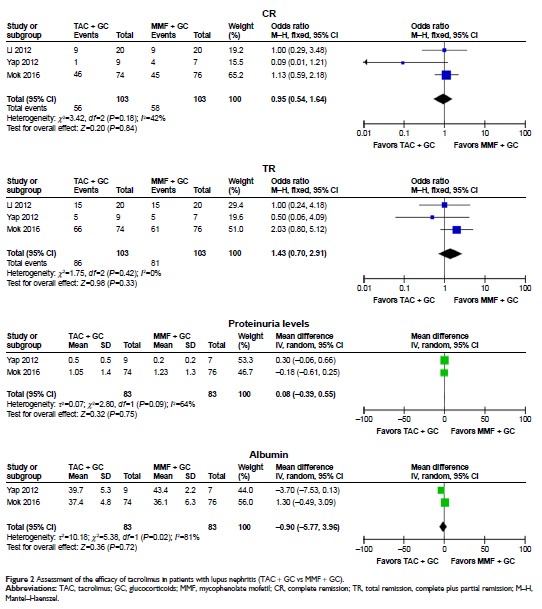
therapeutic regimen comprising TAC + GC vs mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) + GC,
the results indicated that the difference of CR, TR, proteinuria levels, and
albumin between TAC group and MMF group were not significant (all P >0.05). In the
therapeutic regimen comprising TAC + MMF + GC vs CYC + GC, multitarget therapy
group showed higher values of CR, TR, urinary protein decline, and rise of
serum albumin when compared with CYC group (all P <0.05).
Conclusion: TAC is an
effective and safe agent in induction therapy of patients with lupus nephritis.
Keywords: tacrolimus,
lupus nephritis, complete remission, CR, total remission, TR, meta-analysis