9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

利妥昔单抗治疗狼疮性肾炎的临床疗效和安全性
Authors Zhong Z, Li H, Zhong H, Zhou T
Received 18 November 2018
Accepted for publication 25 January 2019
Published 11 March 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 845—856
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S195113
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Background: Long-term
treatment programs with low toxicity represent a therapeutic challenge in lupus
nephritis (LN). Although a therapeutic benefit of rituximab (RTX) has been
reported in LN patients who have failed conventional treatment, the results are
controversial. We aimed to assess the clinical efficacy and safety of RTX as a
new immunosuppressive medicine in the treatment of LN with a meta-analysis.
Methods: Based on
predetermined criteria, PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library were used to
identify the eligible studies. Cochrane Review Manager version 5.3 was applied
to pool the data extracted from individual investigations and provide summary
effect estimates.
Results: Twenty-four
studies with 940 patients were analyzed. In case series trials with specific LN
assessment, the complete remission (CR) rate at 12 months was 35.9% (95% CI:
24.2%–49.5%), and total remission (TR: CR plus partial remission) was 73.4%
(95% CI: 66.0%–79.7%). In controlled trials, RTX was associated with a higher probability
of TR (OR =2.02, 95% CI: 1.23–3.32, P <0.01). The CR in the RTX group was higher than
that in the control group, although there was no significant difference between
the two groups (OR =1.98, 95% CI: 0.90–4.39, P >0.05).
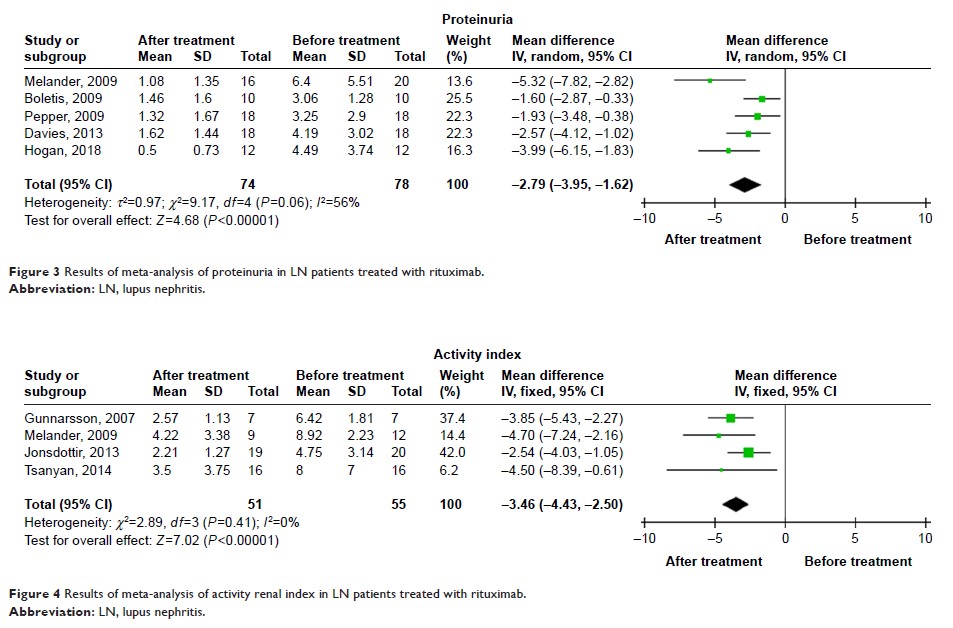
Additionally, RTX treatment significantly decreased proteinuria (mean
difference: -2.79, 95% CI: -3.95 to -1.62, P <0.01) as well
as the renal activity index in patients with LN (mean difference: -3.46, 95%
CI: -4.43 to -2.50, P <0.01). In controlled trials, the relative risks
of the adverse events of infection and infusion reaction were not notably
different between the two groups.
Conclusion: RTX is a
promising therapy for the treatment of LN due to significant clinical efficacy
and a favorable safety profile. In future studies, larger study populations and
longer-term time points may identify additional important patient-centered
outcomes.
Keywords: systemic
lupus erythematosus, lupus nephritis, rituximab, efficacy, safety,
meta-analysis