9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

急性髓性白血病的耐药机制
Authors Zhang J, Gu Y, Chen B
Received 20 October 2018
Accepted for publication 18 January 2019
Published 11 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1937—1945
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S191621
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
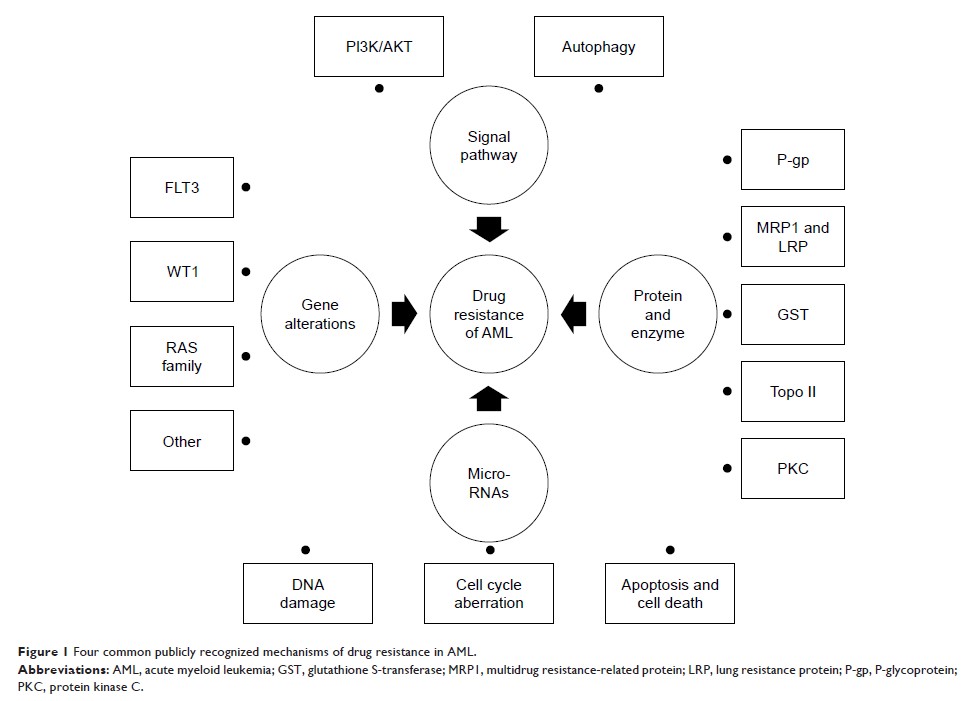
Abstract: Acute
myeloid leukemia (AML) is a kind of malignant hematopoietic system disease
characterized by abnormal proliferation, poor cell differentiation, and
infiltration of bone marrow, peripheral blood, or other tissues. To date, the
first-line treatment of AML is still based on daunorubicin and cytosine
arabinoside or idarubicin and cytosine arabinoside regimen. However, the
complete remission rate of AML is still not optimistic, especially in elderly
patients, and the recurrence rate after complete remission is still high. The
resistance of leukemia cells to chemotherapy drugs becomes the main obstacle in
the treatment of AML. At present, the research on the mechanisms of drug
resistance in AML is very active. This article will elaborate on the main
mechanisms of drug resistance currently being studied, including drug
resistance-related proteins and enzymes, gene alterations, micro RNAs, and
signal pathways.
Keywords: drug
resistance, P-glycoprotein, gene alterations, signaling pathway