9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

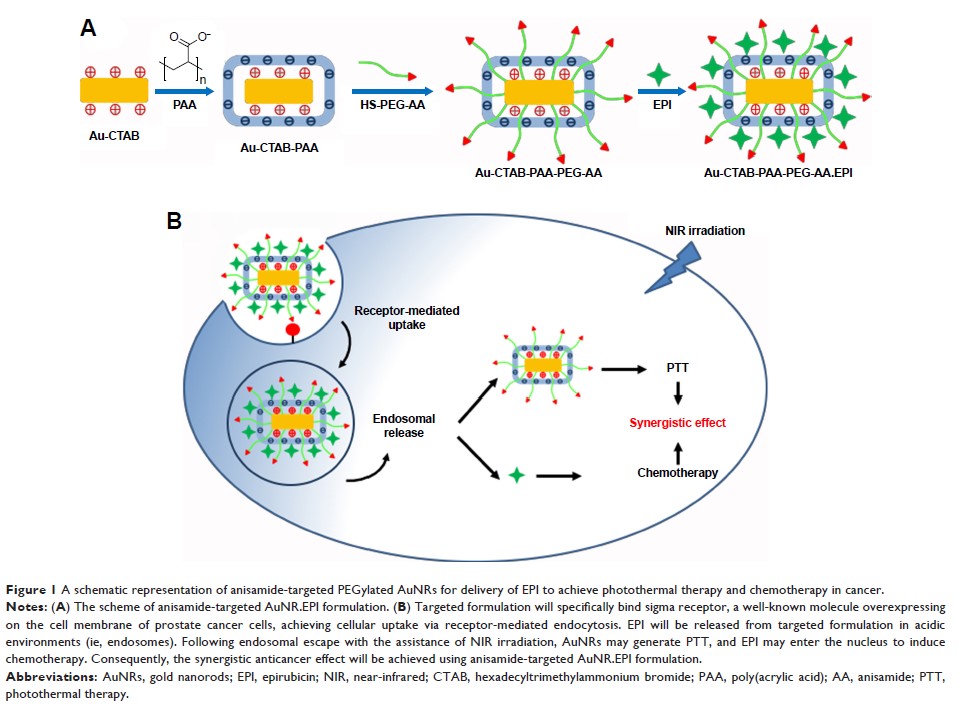
开发针对茴香酰胺的聚乙二醇化金纳米棒用于递送表阿霉素,以用于荷瘤小鼠的化学光热疗法
Authors Wang L, Pei J, Cong Z, Zou Y, Sun T, Davitt F, Garcia-Gil A, Holmes JD, O’Driscoll CM, Rahme K, Guo J
Received 28 October 2018
Accepted for publication 3 February 2019
Published 8 March 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1817—1833
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S192520
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Gold
nanorods (AuNRs), due to the optical and electronic properties namely the
surface plasma resonance, have been developed to achieve the light-mediated
photothermal therapy (PTT) for cancer. However, PTT alone may suffer from
inefficient tumor killing. Recently, the combination of PTT and chemotherapy
has been utilized to achieve synergistic anticancer effects.
Methods: In this
study, AuNRs capped with hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB),
poly(acrylic acid) (PAA), and PEGylated anisamide (a ligand known to target the
sigma receptor) have been developed to produce a range of negatively charged
anisamide-targeted PEGylated AuNRs (namely Au-CTAB-PAA-PEG-AA) for the
combination of PTT and chemotherapy (termed as chemo-photothermal therapy
[CPTT]). Epirubicin (EPI, an anthracycline drug) was efficiently loaded onto
the surface of Au800-CTAB-PAA-PEG-AA
via the electrostatic interaction forming Au800-CTAB-PAA-PEG-AA.EPI
complex.
Results: The
resultant complex demonstrated pH-dependent drug release, facilitated nucleus
trafficking of EPI, and induced antiproliferative effects in human prostate
cancer PC-3 cells. When Au800-CTAB-PAA-PEG-AA.EPI
complex was further stimulated with desired laser irradiation, the synergistic
outcome was evident in PC-3 xenograft mice.
Conclusion: These
results demonstrate a promising strategy for clinical application of CPTT in
cancer.
Keywords: gold
nanoparticles, non-viral drug delivery, chemotherapy, photothermal therapy,
synergistic effect