9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

超声微泡联合壳聚糖修饰的负载多粘菌素 B 的脂质体对有生物膜形成能力的鲍曼不动杆菌的协同抑菌作用
Authors Fu Y, Zhang L, Yang Y, Liu C, He Y, Li P, Yu X
Received 5 September 2018
Accepted for publication 3 February 2019
Published 8 March 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1805—1815
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S186571
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Purpose: Resistant
strains of Acinetobacter
baumannii (AB) that can form biofilms are resistant to polymyxin.
Therefore, effective and safe polymyxin preparations against biofilm-producing
AB are urgently needed. This study aims to prepare chitosan-modified polymyxin
B-loaded liposomes (CLPs) and ultrasound microbubbles (USMBs) and then explore
the synergistic antibacterial effects of USMBs combined with CLPs in vitro.
Methods: CLPs were
prepared using a modified injection method, and microbubbles were prepared
using a simple mechanical vibration method. Minimal biofilm inhibitory
concentration (MBIC) of CLPs against resistant biofilm-producing AB was
determined. Antibacterial activities of CLPs with or without USMBs were
analyzed by crystal violet staining and resazurin assays to evaluate biofilm
mass and viable counts, respectively. Then, the anti-biofilm effects of CLPs
with or without USMBs on biofilm-producing AB were confirmed via scanning
electron microscopy (SEM) analysis.
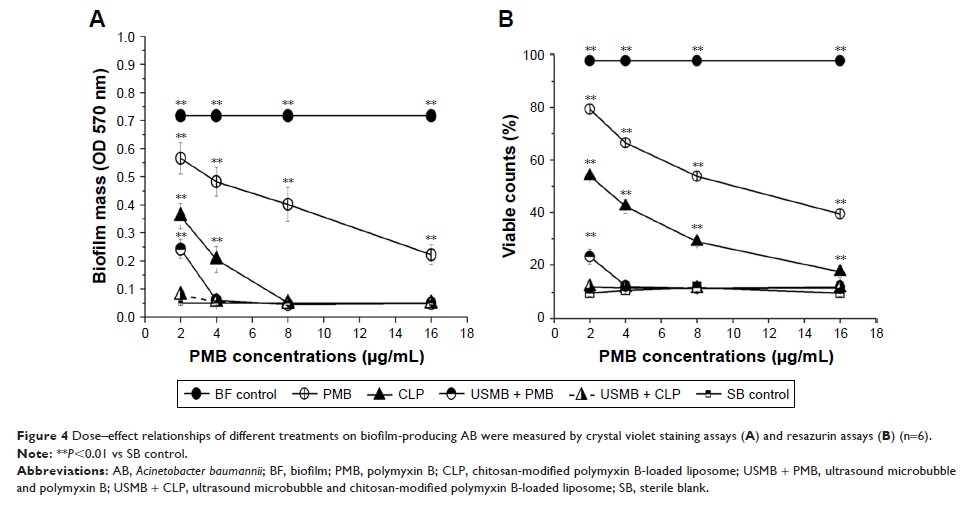
Results: We
prepared CLPs that were 225.17±17.85 nm in size and carried positive charges of
12.64±1.44 mV. These CLPs, with higher encapsulation efficiency and drug
loading, could exhibit a sustained release effect. We prepared microbubbles
that were 2.391±0.052 µm in size and carried negative charges of -4.32±0.43 mV.
The MBICs of the CLPs on the biofilm-producing AB was 8±2 µg/mL, while that of
polymyxin B was 32±2 µg/mL. USMBs in combination with 2 µg/mL of polymyxin B
could completely eliminate the biofilm-producing AB and achieve the maximum
antimicrobial effects (P >0.05 vs sterile blank control). SEM imaging
revealed some scattered bacteria without a biofilm structure in the USMB
combined with the CLP group, confirming that this combination has the greatest
anti-biofilm effects.
Conclusion: In this
research, we successfully prepared USMBs and CLPs that have a more significant
antibacterial effect on biofilm-forming AB than polymyxin B alone. Experiments
in vitro indicate that the synergistic antibacterial effect of combining USMBs
with CLPs containing as little as 2 µg/mL of polymyxin B is sufficient to
almost eliminate drug-resistant biofilm-producing AB.
Keywords: liposome,
chitosan, polymyxin B, ultrasound microbubbles, Acinetobacter baumannii,
biofilms