9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

长链非编码 RNA STXBP5-AS1 通过抑制胃癌细胞的 PI3K/AKT 信号通路抑制细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Cen D, Huang H, Yang L, Guo K, Zhang J
Received 13 November 2018
Accepted for publication 6 February 2019
Published 8 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1929—1936
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S194463
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Introduction: Poor
prognosis of gastric cancer (GC) has partly been a result of late diagnosis due
to nonspecific symptoms in the early stages. The overall survival rate of
patients with GC is quite low. Here, we presented the functional role and
potential mechanism of long noncoding RNA STXBP5-AS1 in GC.
Materials and methods: CCK-8,
scratch wound healing and Transwell assays were conducted to analyze
proliferation, migration, and invasion of SGC7901 and MKN45 cells. Real-time
polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and Western blot assays were performed to
investigate the relationship between STXBP5-AS1 and STXBP5. Finally, the
correlation between STXBP5-AS1 and phosphorylated AKT1 (p-AKT1) was explored to
reveal the potential mechanism of STXBP5-AS1 in GC. Western blot assays were
performed to analyze phosphorylated AKT1 (p-AKT1) and AKT levels.
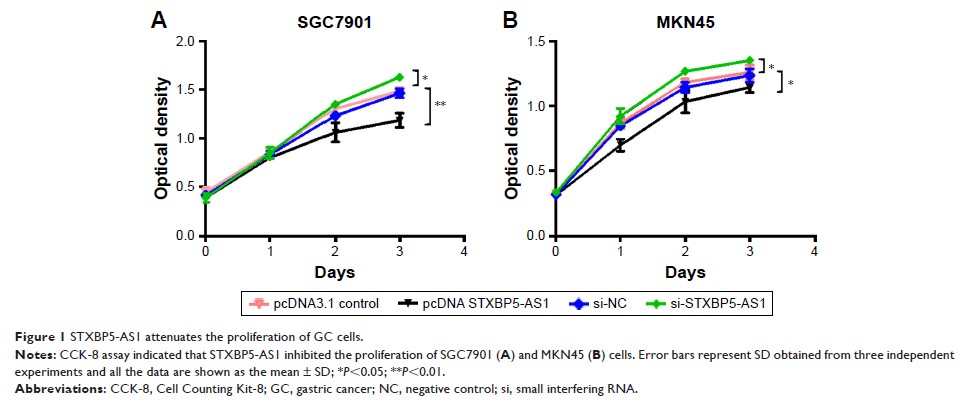
Results: Our
results suggested that STXBP5-AS1 suppressed proliferation, migration, and
invasion, and the upregulation of STXBP5-AS1 significantly repressed STXBP5
expression, and knockdown of STXBP5-AS1 promoted STXBP5 expression. In
addition, the p-AKT1 level decreased when STXBP5-AS1 was overexpressed and the
p-AKT1 level increased with STXBP5-AS1 knockdown in SGC7901 and MKN45 cells.
Conclusion: In
summary, our results indicate that STXBP5-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation,
migration, and invasion through PI3K/AKT in GC.
Keywords: long
noncoding RNA, STXBP5-AS1, STXBP5, PI3K/AKT, GC