9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用 CRISPR/Cas9 技术在 HEp-2 细胞中构建 GLUT-1 和 HIF-1α 基因敲除细胞模型
Authors Lu ZJ, Yu Q, Zhou SH, Fan J, Shen LF, Bao YY, Wu TT, Zhou ML, Huang YP
Received 14 August 2018
Accepted for publication 15 January 2019
Published 8 March 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2087—2096
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S183859
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Glucose transporter
(GLUT)-mediated glucose uptake is an important process in the development of
laryngeal carcinoma, one of the most common malignancies of the head and neck.
GLUT-1, together with HIF-1α, is also an indicator of hypoxia. Both proteins
play a critical role in glucose uptake and glycolysis in laryngeal carcinoma
cells under hypoxic stress. A double gene knockout model in which HIF-1α and GLUT-1 are no
longer expressed can provide important information about carcinogenesis in
laryngeal carcinoma.
Purpose: In this
study we used the CRISPR/Cas 9 system to induce HIF-1α and GLUT-1 double gene
knockout in HEp-2 cells and then used the knocked-out cells to study the role
of these markers in laryngeal carcinoma, including in chemo-radioresistance.
Methods: High-grade
small-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) of HIF-1α and GLUT-1 were designed using an online
tool and inserted into the pUC57-T7-gRNA vector. The recombinant plasmids were
transfected into HEp-2 cells and positive cells were screened using the
dilution method. Gene mutation and expression were determined by sequence
analysis and immunoblotting.
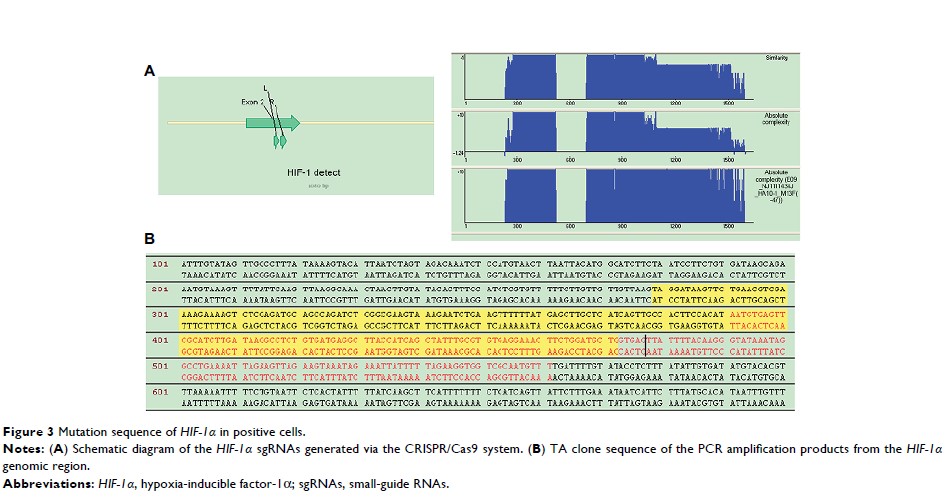
Results: In HIF-1α
and GLUT-1 double gene knockout HEp-2 cells, a 171-bp deletion in the HIF-1α genomic
sequence was detected, whereas multiple base insertions resulted in frameshift
mutations in the GLUT-1 gene. Neither HIF-1α nor GLUT-1 protein
was expressed in positive cells. The proliferation, migration, and invasion of
HEp-2 cells were significantly decreased afterward. The possible mechanism may
be that the inhibition PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway by HIF-1α and GLUT-1double gene
knockout using CRISPR/Cas9 technique lead to reduction of glucose uptake and
lactic acid generation.
Conclusion: Our HIF-1α and GLUT-1 double
gene knockout HEp-2 cell model, obtained using a CRISPR/Cas9-based system, may
facilitate studies of the pathogenesis of laryngeal carcinoma.
Keywords: CRISPR,
Cas9 system, glucose transporter-1, HEp-2 cells, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α,
PI3K, AKT, mTOR pathway, laryngeal carcinoma