9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

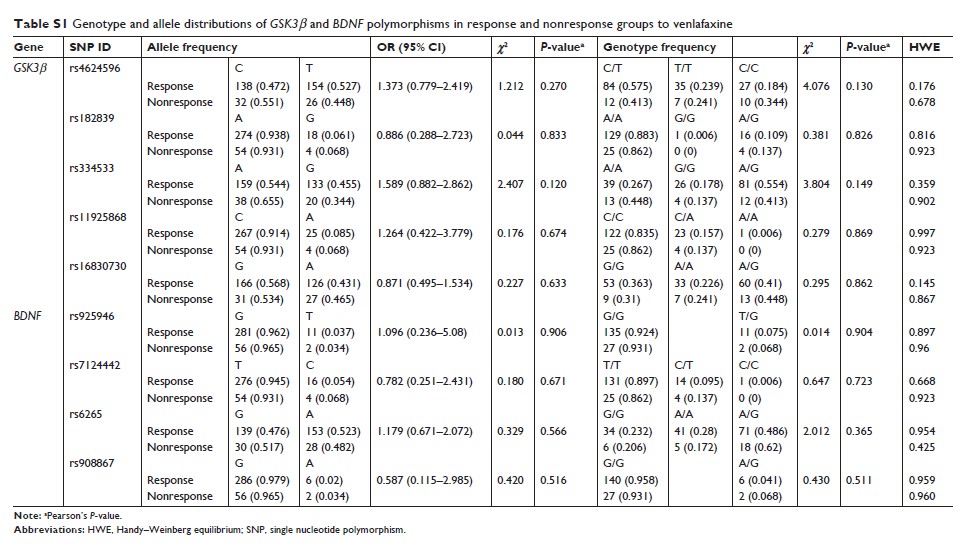
GSK-3β 和 BDNF 基因可能与中国汉族人群对文拉法辛治疗的反应无关
Authors Sun Q, Yuan F, Ren D, Ma G, Yang F, Wu X, He L, He G
Received 18 October 2018
Accepted for publication 28 December 2018
Published 7 March 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 657—661
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S191376
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Purpose: Venlafaxine
is one of the commonly prescribed antidepressants for major depressive disorder
(MDD). Accumulated evidence revealed the involvement of glutamatergic system in
the pathophysiology of MDD and antidepressant treatment.
Methods: We
recruited 193 MDD patients who have been taking venlafaxine for 6 weeks, and
investigated whether single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in GSK-3β and BDNF were associated
with treatment response. Nine SNPs were selected randomly depending on
association studies. Efficacy of treatment was determined by 17-item Hamilton
Rating Scale. Allele and genotype frequencies were compared between responders
and nonresponders.
Results: After
adjusting the false discovery rate, no significant difference was observed
between response and nonresponse groups in allele or genotype distributions
after venlafaxine treatment for 6 weeks.
Conclusion: Our
results indicated that genetic variants in the GSK-3β and BDNF may not
be associated with treatment response in MDD patients treated with venlafaxine.
Keywords: association, GSK-3β , BDNF , major
depressive disorder, venlafaxine