9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

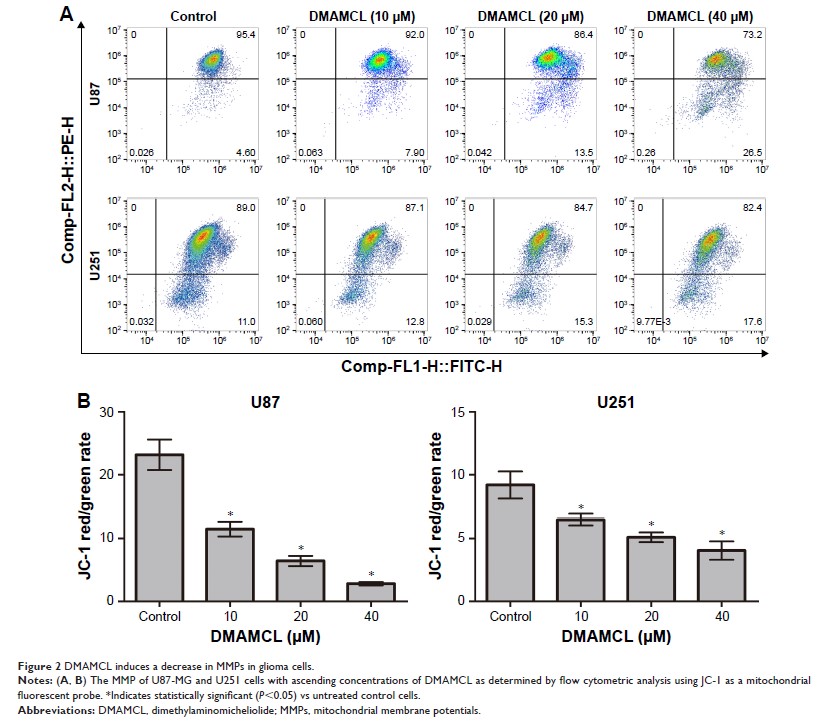
ROS 产生和自噬体积聚通过调节 ROS/MAPK 信号通路和抑制 Akt/mTOR 信号通路,促进由 DMAMCL 诱导的胶质瘤细胞增殖抑制
Authors Wang Y, Zhang J, Yang Y, Liu Q, Xu G, Zhang R, Pang Q
Received 20 November 2018
Accepted for publication 1 February 2019
Published 7 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1867—1880
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S195329
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Purpose: Chemotherapy
after surgery can prolong the survival of patients with gliomas.
Dimethylaminomicheliolide (DMAMCL), a novel chemotherapeutic agent, exhibited
antitumor properties in acute myeloid leukemia stem cells and showed an
increased drug concentration in the brain. This study aims to investigate the
specific anticancer activities and mechanisms of DMAMCL in glioma cells.
Materials and methods: In this
study, the effects of DMAMCL were evaluated and characterized in U87-MG and
U251 glioma cells. Cell viability was assessed by Cell Counting Kit-8.
Apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential, and intracellular reactive oxygen
species (ROS) generation were assessed by fluorescence microscopy.
Autophagosome formation was observed with transmission electron microscopy, and
the autophagy flux was measured by transfecting cells with mRFP-GFP-LC3
adenoviral vectors. Immunofluorescence and Western blot analyses were used to
determine the expression of proteins.
Results: In the
present study, treatment with DMAMCL decreased cell viability and induced
apoptosis in U87-MG and U251 glioma cells. Additionally, DMAMCL activated
autophagy-mediated cell death as evidenced by the formation of autophagosomes,
accumulation of LC3B-II, inhibition of autophagy flux, and increase in cell
viability after cotreatment with an autophagy inhibitor. Subsequent experiments
showed that the DMAMCL-induced apoptosis and autophagy were possibly mediated
by ROS generation and Akt/mTOR signaling pathway inhibition. On the other hand,
the ROS scavenger N-acetyl-l-cysteine and the Akt activator insulin-like growth
factor-1 attenuated the DMAMCL-induced autophagy and cell death.
Conclusion: Our
findings revealed that DMAMCL induced apoptosis and autophagic cell death by
regulating the ROS/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway and
suppressing the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human glioma cells. DMAMCL may be
a novel effective anticancer agent, which can target gliomas.
Keywords: DMAMCL,
apoptosis, autophagy, ROS, glioma