108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

遍在蛋白特异性的蛋白酶 4 通过激活 ERK 通路促进多形性胶质母细胞瘤
Authors Zhou Y, Liang P, Ji W, Yu Z, Chen H, Jiang L
Received 7 June 2018
Accepted for publication 16 December 2018
Published 5 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1825—1839
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S176582
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianmin Xu
Background: Glioblastoma
multiforme (GBM) is one of the most common brain tumors in adults. Current treatments
cannot increase survival to a large extent, as the glioblastoma development
mechanisms remain unknown. It has been well documented that ubiquitination
contributes to tumor initiation and/or progression in many kinds of cancer.
Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 (USP4), a member of deubiquitinating enzymes
(DUBs) family, can remove ubiquitin residues and play a role in cancer
development.
Methods: In the
current study, lentiviruses were used to manipulate the expression of USP4.
Real-time PCR and Western blot were used to measure the expression level of
USP4. Then, CCK-8 and annexin-V staining were used to detect cell proliferation
and cell apoptosis, respectively.
Results: First, we
found that USP4 was highly upregulated in GBM tissues in comparison with that
in normal tissues and high level of USP4 correlated with poor prognosis.
Moreover, knockdown of USP4 could significantly inhibit cell proliferation and
increase cell apoptosis in U87 and T98G cells. Cells with stable USP4 reduction
exhibited slower tumor growth rate and smaller tumor size than the control
group cells in a xenograft mouse model. Inhibition of USP4 downregulated the
expression of PCNA, Bcl-2 and p-ERK1/2, but upregulated the expression of Bax
both in vitro and in vivo. Inversely, USP4 overexpression could
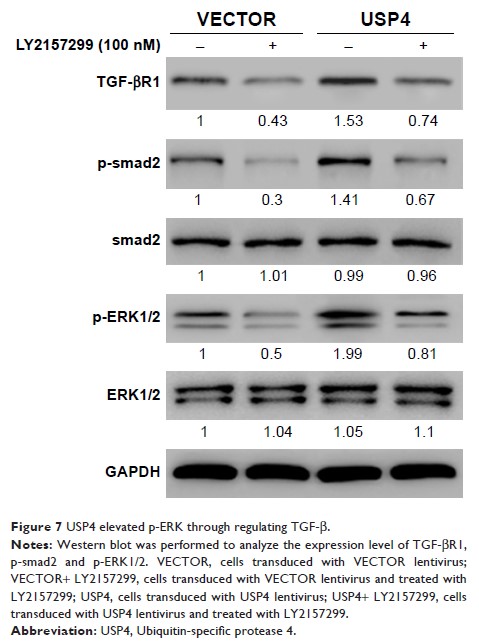
attenuate the effects contributed by ERK inhibitor. TGF-βR inhibition reduced
level of TGF-βR1, p-smad2 and p-ERK1/2 which can partially be rescued by USP4
overexpression.
Conclusion: USP4, as
a potential novel oncogene, promotes GBM by activation of ERK pathway through
regulating TGF-β.
Keywords: USP4,
GBM, ERK, ubiquitin