108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

白藜芦醇通过激活 PI3K/Akt 和 SIRT1/PGC1α 通路抑制紫杉醇诱导的神经病理性疼痛
Authors Li X, Yang S, Wang L, Liu P, Zhao S, Li H, Jiang Y, Guo Y, Wang X
Received 30 August 2018
Accepted for publication 4 January 2019
Published 4 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 879—890
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S185873
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
Background: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) is one of the essential signaling
pathways for the development and maintenance of neuropathic pain.
Objective: To
investigate the effect of resveratrol (RES) on paclitaxel-induced neuropathic
pain in rats and elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms.
Method: Male
Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into seven groups (n=10/group): Group
C, Group P, Group R, Group R+P, Group LY + R+P, Group LY (the specific
inhibitor of PI3K), Group E (the specific inhibitor of sirtuin 1 [Sirt1]). Paw
withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWT) and thermal withdrawal latency (TWL) were
recorded. Mitochondrial histomorphology was performed by transmission electron
microscope. PI3K, p-Akt, and t-Akt expressions were tested using
immunohistochemistry. Western blot was used to detect p-Akt, t-Akt, SIRT1, and
PGC1α expressions. The apoptosis in the striatum, spinal dorsal horns (SDH),
and dorsal root ganglions (DRG) tissues was assayed by TUNEL. ELISA was used to
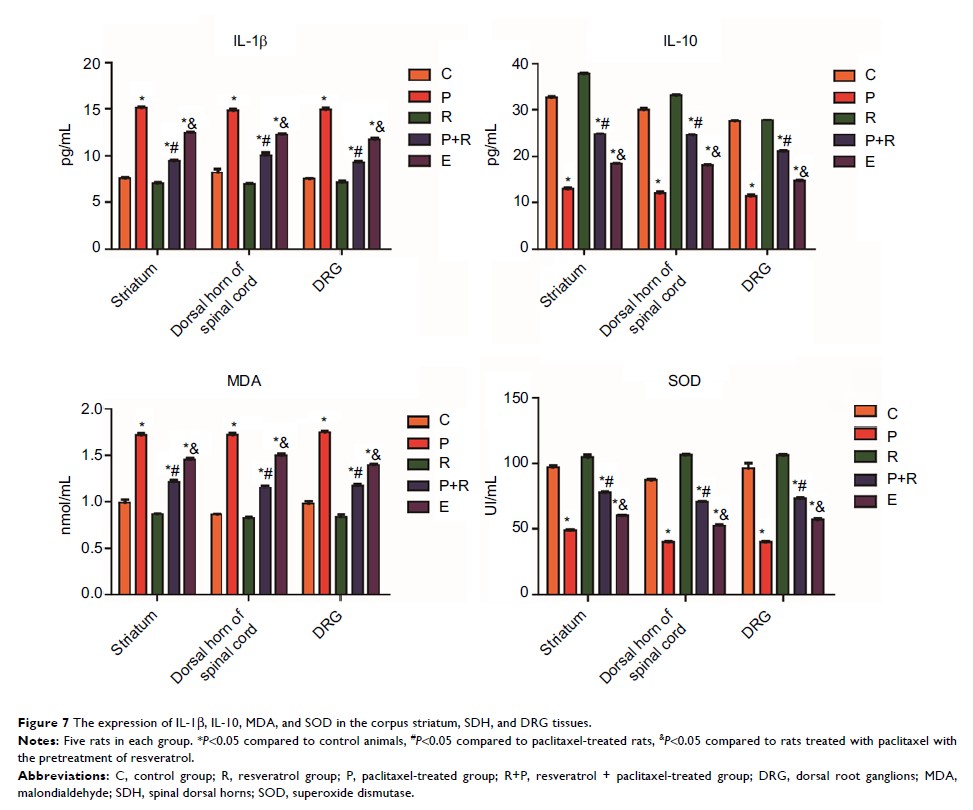
detect the contents of IL-β, IL-10, malondialdehyde (MDA), and superoxide
dismutase (SOD) in striatum, SDH, and DRG tissues.
Results: Compared
to the control group, PWT and TWL in the P and LY +R+P groups were
significantly decreased on 8th and 14th day after paclitaxel administration (P <0.05). The
expressions of p-Akt, SIRT1, and PGC1α were decreased in paclitaxel-induced
neuropathic rats; however, the expressions of p-Akt, SIRT1, and PGC1α were
significantly increased after RES treatment (P <0.05). Furthermore, the expression of p-Akt was
decreased by LY294002 (P <0.05), and amount of SIRT1 and PGC1α expression
was inhibited by EX-527 (P <0.05). The t-Akt level was not significantly
changed in all groups. RES prevented paclitaxel-induced mitochondrial damage by
PI3K/Akt. RES improves the pain symptoms of paclitaxel neuralgia rats by
increasing the IL-10 and decreasing the expression of IL-1β. RES increases the
SOD and reduces the MDA. RES reduces apoptosis by SIRT1/PGC1α signal pathway.
Conclusion: Our results
suggest that RES may inhibit paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain via PI3K/Akt
and SIRT1/PGC1α pathways.
Keywords: resveratrol,
paclitaxel, neuropathic pain, PI3K/Akt, SIRT1/PGC1α