108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

TAZ 的基因消融通过激活 CaMKII/MIEF1 信号通路诱导 HepG2 肝癌细胞凋亡
Authors Hou Y, Lan C, Kong Y, Zhu C, Peng W, Huang Z, Zhang C
Received 27 November 2018
Accepted for publication 3 February 2019
Published 1 March 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1765—1779
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S196142
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background and objective: Transcriptional
coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) has been found to be associated with
tumor progression. Mitochondrial homeostasis regulates cancer cell viability
and metastasis. However, the roles of TAZ and mitochondrial homeostasis in
liver cancer viability have not been explored. The aim of our study was to
investigate the influence of TAZ on HepG2 liver cancer cell apoptosis.
Materials and methods: HepG2
liver cancer cell was used in the present study, and shRNA against TAZ was
transfected into HepG2 cell to knockdown TAZ expression. Mitochondrial function
was analyzed using Western blotting, immunofluorescence assay, and flow
cytometry. Pathway blocker was used to confirm the role of CaMKII pathway in
TAZ-mediated cancer cell death.
Results: Our
results indicated that TAZ deletion induced death in HepG2 cell via apoptosis.
Biological analysis demonstrated that mitochondrial stress, including
mitochondrial bioenergetics disorder, mitochondrial oxidative stress, and
mitochondrial apoptosis, were activated by TAZ deletion. Furthermore, we found
that TAZ affected mitochondrial stress by triggering mitochondrial elongation
factor 1 (MIEF1)-related mitochondrial dysfunction. The loss of MIEF1 sustained
mitochondrial function and promoted cancer cell survival. Molecular
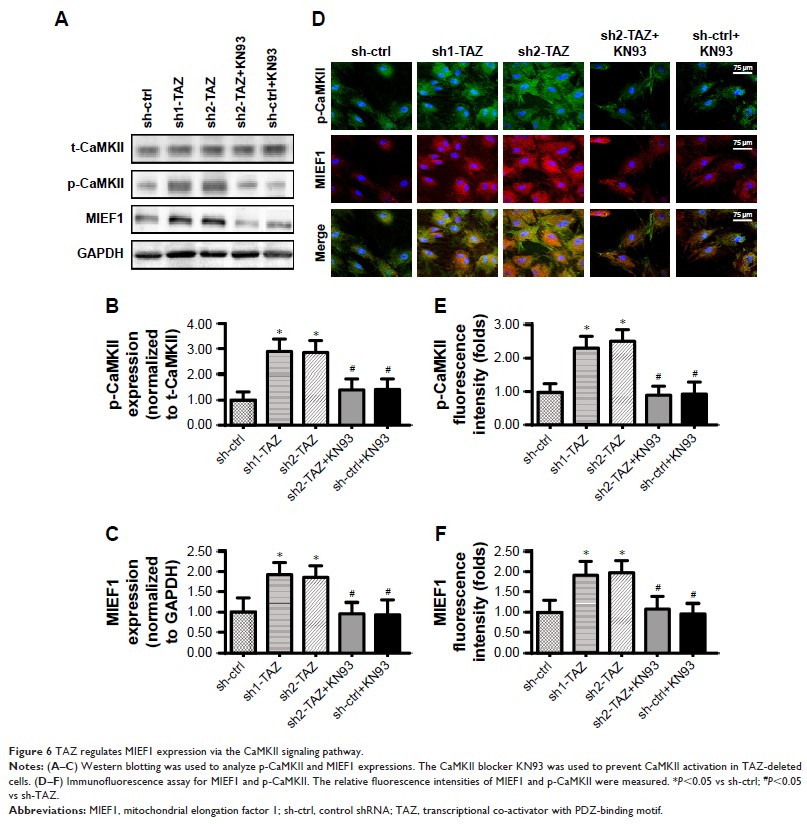
investigation illustrated that TAZ regulated MIEF1 expression via the CaMKII
signaling pathway. Blockade of the CaMKII pathway prevented TAZ-mediated MIEF1
upregulation and improved cancer cell survival.
Conclusion: Taken
together, our results highlight the key role of TAZ as a master regulator of
HepG2 liver cancer cell viability via the modulation of MIEF1-related
mitochondrial stress and the CaMKII signaling pathway. These findings define
TAZ and MIEF1-related mitochondrial dysfunction as tumor suppressors that act
by promoting cancer apoptosis via the CaMKII signaling pathway, with potential
implications for new approaches to liver cancer therapy.
Keywords: TAZ,
liver cancer, death, MIEF1, CaMKII signaling pathway