108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

EGFR 突变与非小细胞肺癌患者的内脏胸膜侵犯发展显着相关
Authors Shi J, Yang Y, Zhao Y, Zhu J, Song X, Jiang G
Received 24 November 2018
Accepted for publication 31 January 2019
Published 1 March 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1945—1957
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S195747
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objectives: A
retrospective study was performed to investigate the association between EGFR mutations and
visceral pleural invasion (VPI), and evaluate the prognostic value of EGFR in
resected non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with VPI.
Materials and methods: Clinicopathological
characteristics and follow-up information were collected from 508 consecutive
patients with surgically resected stage I–III NSCLC, and EGFR mutations
were detected based on real-time PCR technology. Significant results (P <0.05) from
univariate logistic regression analysis were involved as covariates to adjust
confounding factors in the analysis of independent factors.
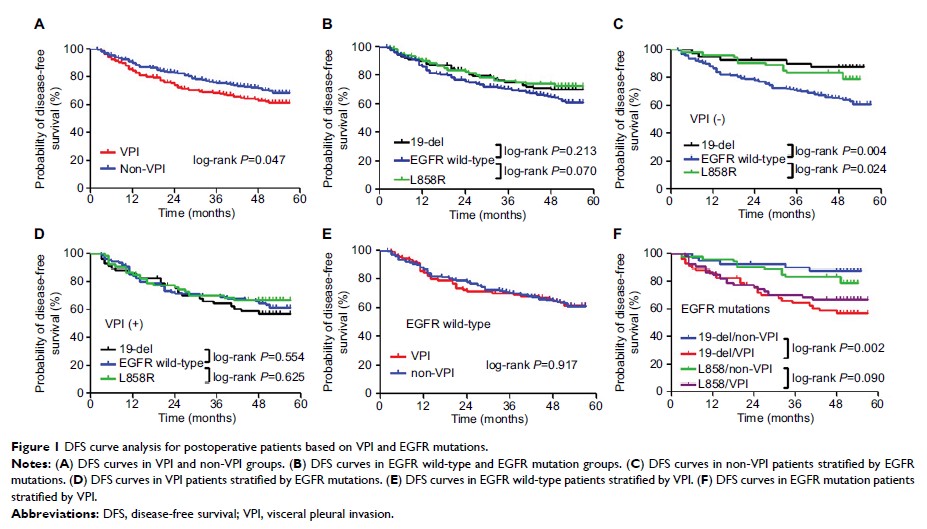
Results: VPI
and EGFR mutations
were detected in 229 (45.1%) and 243 (47.8%) cases in NSCLC, respectively.
There was a significant association between EGFR mutations
and VPI development. Both 19-del (adjusted OR =2.13, 95%CI =1.13–3.99, P =0.019) and L858R
(adjusted OR =2.89, 95%CI =1.59–5.29, P =0.001) could significantly increase the risk of VPI
development compared with EGFR wild-type. Higher frequency of L858R (adjusted OR
=2.63, 95%CI =1.42–4.88, P =0.002) was detected in VPI patients compared with
non-VPI patients. 19-del (adjusted HR =0.31, 95%CI =0.12–0.80, P =0.015) was an
independent prognostic factor for a better disease-free survival (DFS) in
non-VPI patients. No significant association was shown between EGFR mutations
and DFS in VPI patients.
Conclusion: EGFR mutations
were significantly associated with VPI development in NSCLC, but no significant
association was observed between EGFR mutations and DFS in the patients with
VPI. 19-del was a favorable prognostic factor for DFS in non-VPI patients.
Keywords: EGFR mutations,
visceral pleural invasion, non-small-cell lung cancer, association study