108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

酸响应性纳米粒子作为结肠癌的新型氧化应激诱导抗癌治疗剂
Authors Zhao C, Cao W, Zheng H, Xiao Z, Hu J, Yang L, Chen M, Liang G, Zheng S, Zhao C
Received 6 October 2018
Accepted for publication 7 January 2019
Published 28 February 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1597—1618
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S189923
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
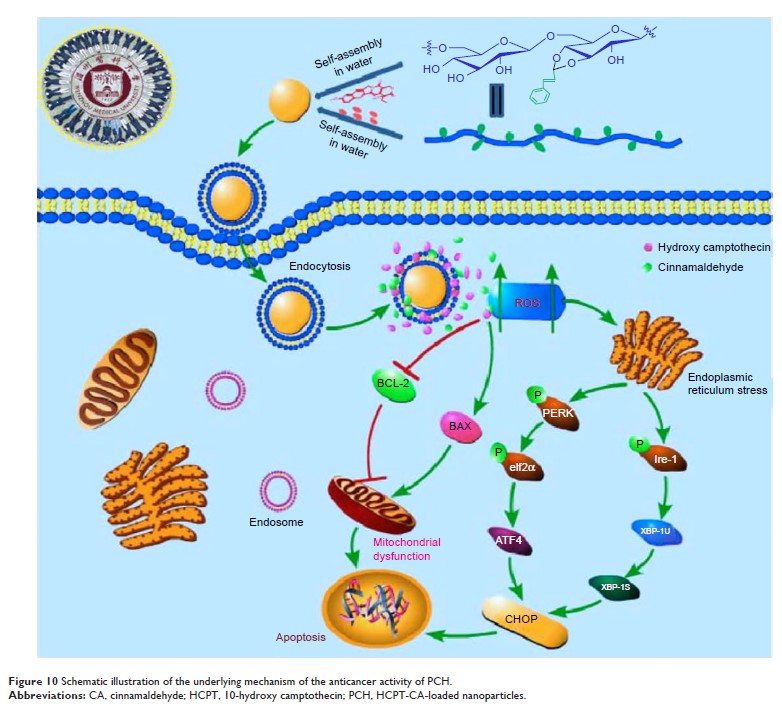
Objective: Nanoparticles
can efficiently carry and deliver anticancer agents to tumor sites. Mounting
evidence indicates that many types of cancer cells, including colon cancer,
have a weakly acidic microenvironment and increased levels of reactive oxygen
species. The construction of nano drug delivery vehicles “activatable” in
response to the tumor microenvironment is a new antitumor therapeutic strategy.
Methods: Cinnamaldehyde
(CA) was designed to link directly with dextran to form a polymer through an
acid cleavable acetal bond. Herein, a novel pH-sensitive drug delivery system
was constructed with co-encapsulated 10-hydroxy camptothecin (HCPT). Dynamic
light scattering (DLS) analysis, transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
analysis, and release kinetics analysis of HCPT-CA-loaded nanoparticles (PCH)
were conducted to investigate the physical and chemical properties. The
cellular uptake signatures of the nanoparticles were observed by confocal
microscopy and flow cytometry. Cell viability, cell scratch assay, apoptosis
assay, and colony formation assay were performed to examine the potent
antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of the PCH. The antitumor mechanism of
the treatment with PCH was evaluated by Western blotting, flow cytometry, and
TEM analysis. The pharmacokinetics of PCH were examined in healthy Sprague
Dawley rats within 6 hours after sublingual vein injection. We lastly examined
the biodistribution and the in vivo anticancer activity of PCH using the
xenograft mouse models of HCT116 cells.
Results: Both HCPT
and CA were quickly released by PCH in an acidic microenvironment. PCH not only
induced cancer cell death through the generation of intracellular reactive
oxygen species in vitro but also facilitated the drug uptake, effectively
prolonged drug circulation, and increased accumulation of drug in tumor sites.
More attractively, PCH exhibited excellent therapeutic performance and better
in vivo systemic safety.
Conclusion: Overall,
PCH not only utilized the tumor microenvironment to control drug release,
improve drug pharmacokinetics, and passively target the drug to the tumor
tissue, but also exerted a synergistic anticancer effect. The acid-responsive
PCH has enormous potential as a novel anticancer therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: cinnamaldehyde,
hydroxy camptothecin, ROS, pH-responsive nanoparticles, colon cancer