108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CD24 同型促进细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,在肝细胞癌中通过 EGR1 获得下调
Authors Li L, Chen J, Ge C, Zhao F, Chen T, Tian H, Li J, Li H
Received 30 November 2018
Accepted for publication 18 January 2019
Published 28 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1705—1716
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S196506
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Gaetano Romano
Introduction: CD24 is
known as a heavily glycosylated cell surface molecule that is highly expressed
in a wide variety of human malignancies. Previous studies have shown that CD24
plays an important role in self-renewal, proliferation, migration, invasion and
drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, little is known
about the expression and function of CD24 isoform a (CD24A) and CD24 isoform b
(CD24B) in HCC.
Materials and methods: Quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and Western blotting were performed
to detect CD24 and EGR1 expression in HCC cells and tissue. The function of
CD24 in cell proliferation was verified with MTT assays, colony formation
assays and tumor xenograft models. Wound healing assays and invasion assays
were performed to clarify the function of CD24 in the regulation of cell
migration and invasion in HCC. A dual luciferase reporter assay and chromatin
immunoprecipitation assay were used to analyze the regulation mechanism of
CD24A.
Results: CD24A but
not CD24B, which was barely detected by qPCR and Western blotting, is
significantly upregulated in HCC tissue. Both CD24A and CD24B contribute to HCC
cell proliferation, migration and invasion, but CD24A is more effective than
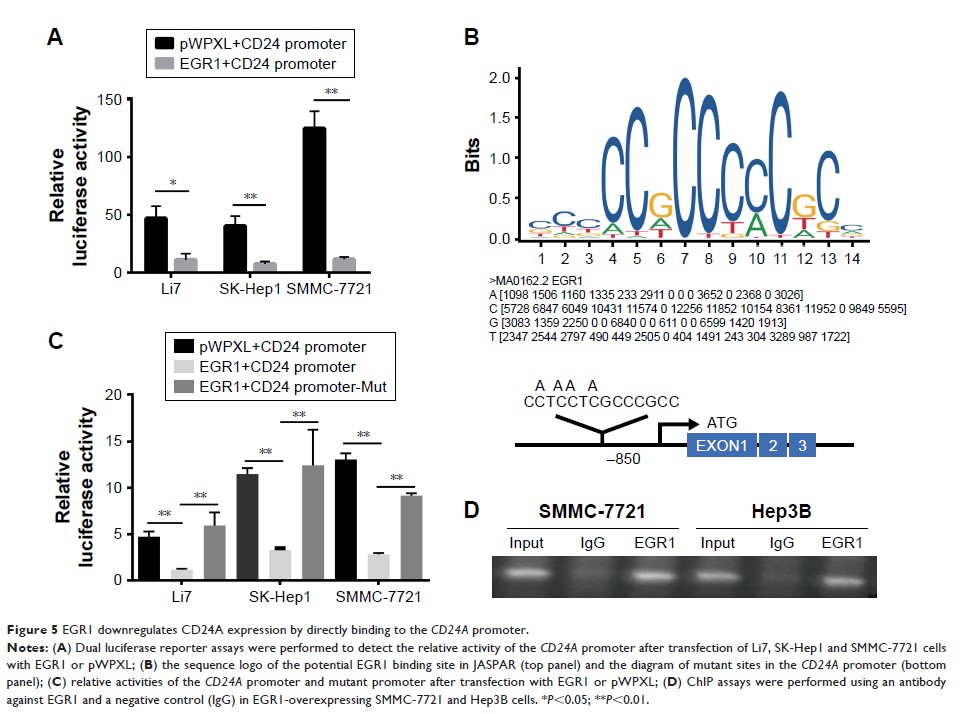
CD24B. EGR1 downregulates CD24A and exerts transcription-promoting activity on
the CD24A promoter.
Furthermore, EGR1 represses HCC cell proliferation via downregulation of CD24A.
Conclusion: CD24A is
the predominant CD24 isoform in HCC and plays a major role in cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion. EGR1 can exert its antitumor effect
through transcriptional downregulation of CD24A in HCC.
Keywords: CD24A,
CD24B, EGR1, proliferation, hepatocellular carcinoma