108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

各种干预措施对血清 γ-谷氨酰转移酶基线分层后出现肝细胞癌大血管侵犯的影响
Authors Liu Y, Zhang Q, Yang X, Li Y, Zhu B, Niu S, Huang Y, Hu Y, Wang X
Received 17 August 2018
Accepted for publication 29 January 2019
Published 28 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1671—1679
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S184302
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Elevated
serum γ-glutamyltransferase (γ-GT) levels are related to an increased cancer
risk and worse prognosis in many cancers. We evaluated the effects of γ-GT
stratification on the occurrence of macrovascular invasion (MVI) in patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who underwent hepatic resection (HR),
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), or TACE combined with
radiofrequency ablation (TACE-RFA).
Patients and methods: A total
of 903 patients with HCC in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage A or B were
included. Of these patients, 118 underwent HR, 445 underwent TACE-RFA, 256
underwent TACE, and 84 patients received conservative treatment only (control
group). γ-GT, albumin, γ-fetoprotein, and intervention were selected as
significant predictive factors for MVI in 1 year by forward selection. The
optimal cutoff value of γ-GT was 39 IU/L according to receiver operating
characteristic analysis, with a sensitivity and specificity of 87.0% and 45.6%,
respectively.
Results: The
1-year MVI incidence of patients with HCC in the group with γ-GT ≥39
IU/L was higher than that of the group with γ-GT <39 IU/L treated with
HR, TACE-RFA, or TACE (P =0.0166, P =0.0041, and P <0.001, respectively). The MVI rates at 1 year
were similar in the group with γ-GT ≥39 IU/L that underwent HR, TACE-RFA,
or TACE and the control group (P =0.4402, P =0.2214, and P =0.4159, respectively). Different effects of various
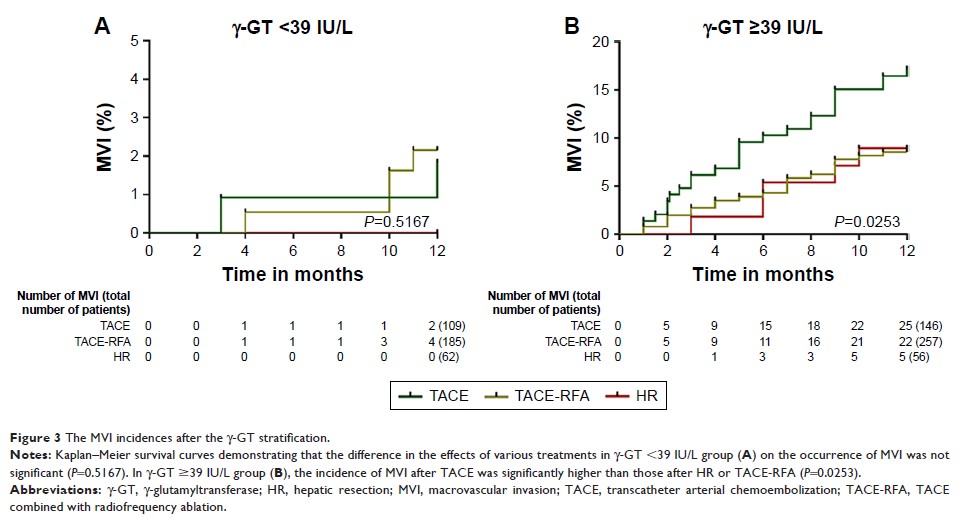
treatments with γ-GT <39 IU/L group on the occurrence of MVI are not
significant (P =0.5167).
However, the incidence of MVI after TACE was significantly higher than
that after HR or TACE-RFA in γ-GT ≥39 IU/L group (P =0.0253).
Conclusion: Baseline
serum γ-GT stratification may help select the appropriate treatment to reduce
the MVI incidence.
Keywords: gamma-glutamyltransferase,
macroscopic vascular invasion, liver cancer