108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ARQ-197 通过减慢其细胞内病原体清除,增强索拉非尼在肝细胞癌细胞中的抗肿瘤作用
Authors Gao X, Chen H, Huang X, Li H, Liu Z, Bo X
Received 1 December 2018
Accepted for publication 24 January 2019
Published 26 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1629—1640
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S196713
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) is one of the heaviest malignant burdens in China. Molecular
targeting agent, sorafenib, is the main therapeutic option for antitumor
therapy of advanced HCC, but it is currently too expensive for the public and
its therapeutic effect does not satisfy initial expectation. Therefore, it is
important to develop more effective molecular targeted therapeutic strategies
for advanced HCC.
Materials and methods: The
antitumor effects of sorafenib or ARQ-197, an antagonist of c-MET
(tyrosine-protein kinase Met or hepatocyte growth factor receptor), were
examined by MTT or in murine tumor model. The effect of ARQ-197 on
epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) or multidrug resistance (MDR) was
examined by quantitative real-time PCR for the expression of related genes. The
clearance of sorafenib in HCC cells was detected by liquid chromatography-mass
spectrometry/mass spectrometry.
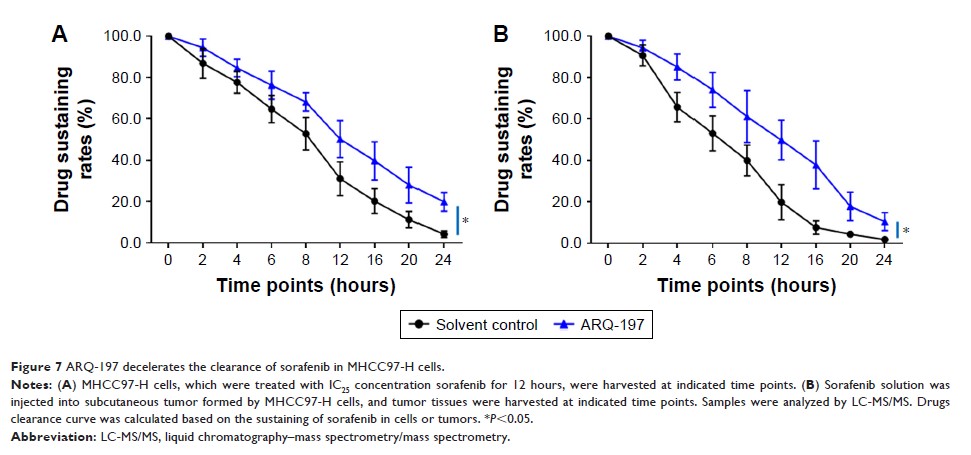
Results: ARQ-197
treatment enhanced the sensitivity of HCC cells to sorafenib. Mechanistic
studies indicated that ARQ-197 inhibited the expression of EMT- and MDR-related
genes. Moreover, ARQ-197 treatment decelerated the clearance of sorafenib in
cultured HCC cells and subcutaneous HCC tumors in nude mice.
Conclusion: In the
present work, our data suggested that ARQ-197 decelerated the clearance of
sorafenib in HCC cells and enhanced the antitumor effect of sorafenib.
Keywords: advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma, molecular targeted agents, ARQ-197 and sorafenib,
drug clearance, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, multidrug resistance