108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

KIF15 通过 MEK-ERK 信号通路促进膀胱癌增殖
Authors Zhao H, Bo Q, Wu Z, Liu Q, Li Y, Zhang N, Guo H, Shi B
Received 22 October 2018
Accepted for publication 7 January 2019
Published 26 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1857—1868
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S191681
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Background: Bladder
cancer (BC) is the most common cancer of the urinary tract and invariably
predicts a poor prognosis. In this study, we found a reliable gene signature
and potential biomarker for predicting clinical prognosis.
Methods: The gene
expression profiles were obtained from the GEO database. By performing GEO2R
analysis, numerous differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were found. Three
different microarray datasets were integrated in order to more precisely
identify up-expression genes. Functional analysis revealed that these genes
were mainly involved in cell cycle, DNA replication and metabolic
pathways.
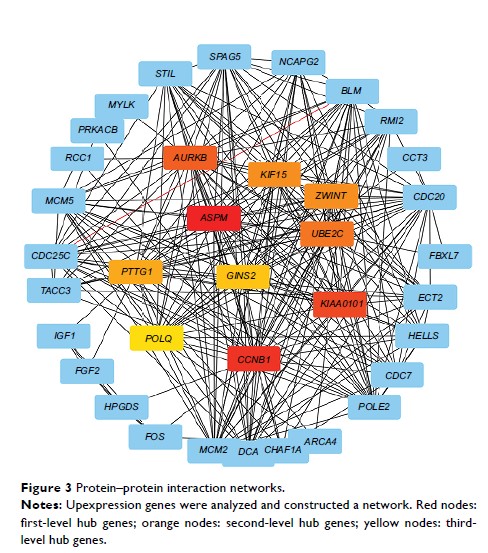
Results: Based on
protein-protein interactome (PPI) networks that were identified in the current
study and previous studies, we focused on KIF15 for further study. The results
showed that KIF15 promotes BC cell proliferation via the MEK -ERK pathway, and
Kaplan‐Meier survival analysis revealed that KIF15 expression was an
independent prognostic risk factor in BC patients.
Conclusion: KIF15 may
represent a promising prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic option
for BC.
Keywords: KIF15,
bladder cancer, proliferation, MEK–ERK