108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

C-C 趋化因子受体7对实体瘤患者预后价值的荟萃分析
Authors Zu G, Luo B, Yang Y, Tan Y, Tang T, Zhang Y, Chen X, Sun D
Received 12 October 2018
Accepted for publication 28 December 2018
Published 26 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1881—1892
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S190510
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: Expression
of C-C chemokine receptor type 7 (CCR7) is associated with the prognosis of
several cancers. The aim of this study was to conduct the meta-analysis to
determine the prognostic value of CCR7 expression in solid tumors.
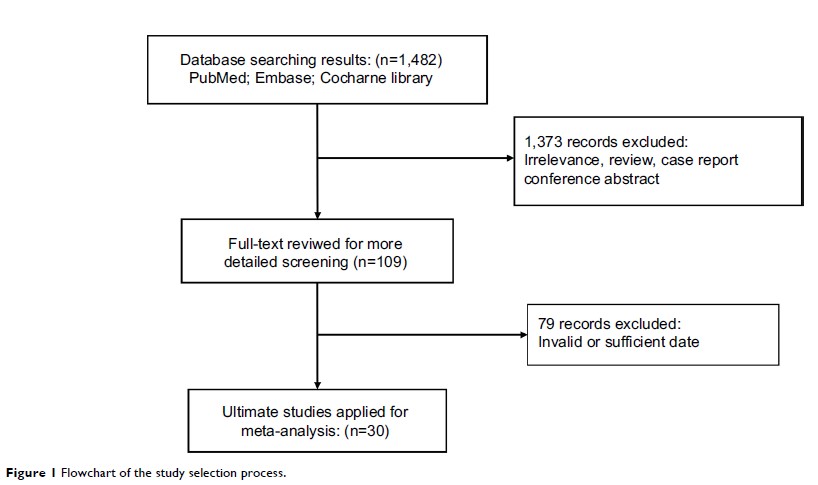
Materials and methods: We
searched for relevant literature in the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library
databases (last updated on January 15, 2018). The associations of CCR7
expression with overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), recurrence-free
survival (RFS), progress-free survival (PFS), and disease-specific survival
(DSS) were estimated.
Results: In total,
30 qualified studies including 3,413 patients were enrolled. The results
revealed that higher expression of CCR7 predicted poorer OS (pooled HR =1.79;
95% CI =1.49–2.16; P <0.001) and PFS (pooled HR =2.18; 95% CI
=1.49–3.18; P <0.001), but was not associated with DFS (pooled
HR =1.69; 95% CI =0.79–3.61; P =0.175), RFS (pooled HR =1.29; 95% CI
=0.48–3.44; P =0.618), or DSS (pooled HR =3.06; 95% CI
=0.38–24.83; P <0.294).
Conclusion: From this
meta-analysis, we concluded that high expression of CCR7 in tumor tissue is
associated with poor survival in patients with solid tumors, and may be a
prognostic biomarker for tumor progression.
Keywords: CCR7,
solid tumors, prognosis, systematic review, meta-analysis