108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

具有神经精神病学表现的迟发性钴胺素 C 疾病患者的临床特征和结果:一个中国病例系列
Authors Wang S, Yan C, Wen B, Zhao Y
Received 4 December 2018
Accepted for publication 23 January 2019
Published 21 February 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 549—555
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S196924
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Objective: The
Cobalamin C (cblC) disease is an inborn error of cobalamin metabolism.
Late-onset cblC disease was diagnosed in patients having overt symptoms after 4
years of age. The late-onset cblC disease patients were rare and easily
misdiagnosed. This study analyzed the clinical presentations, gene mutations,
and treatments of Chinese patients with late-onset cblC disease.
Methods: The
clinical data of 26 Han Chinese patients diagnosed with late-onset cblC disease
were retrospectively analyzed. All patients underwent serum homocysteine level
exam, urine concentrations of organic acids measurement, neuroimaging scans,
gene analysis, and treatments evaluations.
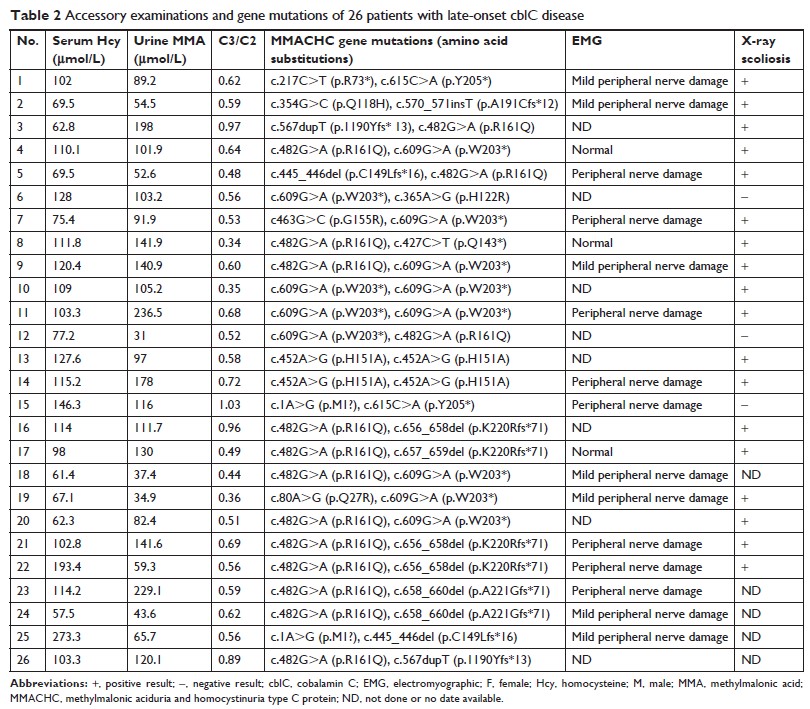
Results: The mean
age at disease onset and diagnosis was 17.8±7.0 years. The most frequent
neuropsychiatric disturbances were lower limb weakness (50%), psychiatric
disturbances (46.2%), and gait instability (42.3%). The mean methylmalonic acid
level in urine was 107.4±56.6 µmol/L, and mean serum total homocysteine was
105.4±41.0 µmol/L. The most common abnormal radioimaging changes were observed
in the spinal cord (88%) and brain (32%). Scoliosis was detected in 85.7% of
patients. The methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type C protein gene
analysis showed that c.482G>A (57.7%) and c.609G>A (34.6%) mutations were
the most frequent genotypes. After treatments with hydroxycobalamin, betaine,
folic acid, L-carnitine, and compound vitamin B, the clinical features and
biochemical parameters of patients with late-onset cblC disease were found to
be alleviated.
Conclusion: In our
late-onset cblC disease cases, lower limb weakness, psychiatric disturbances,
and gait instability were the most frequent manifestations. Patients responded
well to the drug treatments with hydrocobalamin and betaine. When juvenile or
adult patients with hyperhomocysteinemia present with neurological symptoms,
cblC disease needs to be considered.
Keywords: methylmalonic
aciduria, homocysteine, late-onset, neuropsychiatric, cobalamin